Trends in US hospitalizations for anaphylaxis among infants and toddlers: 2006 to 2015
- PMID: 32911059
- PMCID: PMC8686187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.09.003
Trends in US hospitalizations for anaphylaxis among infants and toddlers: 2006 to 2015
Abstract
Background: Anaphylaxis is a potentially fatal acute allergic reaction. Its overall prevalence appears to be rising, but little is known about US hospitalization trends among infants and toddlers.
Objective: To identify the trends and predictors of hospitalization for anaphylaxis among infants and toddlers.
Methods: We used the nationally representative National Inpatient Sample (NIS), from 2006 to 2015, to perform an analysis of trends in US hospitalizations for anaphylaxis among infants and toddlers (age, <3 years) and other children (age, 3-18 years). For internal consistency, we identified patients with anaphylaxis by the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification diagnosis code and excluded those with the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (late 2015). We calculated trends in anaphylaxis hospitalizations over time by age group and then used multivariable logistic regression to describe anaphylaxis hospitalizations among infants and toddlers.
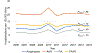
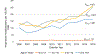
Results: Among infants and toddlers, there was no significant change in anaphylaxis hospitalizations during the 10-year study period (Ptrend = .14). Anaphylaxis hospitalization among infants and toddlers was more likely in males, with private insurance, in the highest income quartile, with chronic pulmonary disease, who presented on a weekend day, to an urban teaching hospital, located in the Northeast. In contrast, anaphylaxis hospitalizations among older children (age, 3-<18 years) rose significantly during the study (Ptrend < .001).
Conclusion: Anaphylaxis hospitalizations among infants and toddlers in the United States were stable from 2006 to 2015, whereas hospitalizations among older children were rising. Future research should focus on the trends in disease prevalence and health care utilization in the understudied population of infants and toddlers.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report—second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(2):391–397. - PubMed
-
- Wood RA, Camargo CA Jr, Lieberman P, et al. Anaphylaxis in America: the prevalence and characteristics of anaphylaxis in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(2):461–467. - PubMed
-
- Greenhawt M, Gupta RS, Meadows JA, et al. Guiding principles for the recognition, diagnosis, and management of infants with anaphylaxis: an expert panel consensus. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(4):1148–1156.e5. - PubMed
-
- Gupta RS, Springston EE, Warrier MR, et al. The prevalence, severity, and distribution of childhood food allergy in the United States. Pediatrics. 2011; 128(1):e9–e17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

