Biosensor and molecular-based methods for the detection of human coronaviruses: A review
- PMID: 32911064
- PMCID: PMC7477626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101662
Biosensor and molecular-based methods for the detection of human coronaviruses: A review
Abstract
The ongoing crisis due to the global pandemic caused by a highly contagious coronavirus (Coronavirus disease - 2019; COVID-19) and the lack of either proven effective therapy or a vaccine has made diagnostic a valuable tool in disease tracking and prevention. The complex nature of this newly emerging virus calls for scientists' attention to find the most reliable, highly sensitive, and selective detection techniques for better control or spread of the disease. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and serology-based tests are currently being used. However, the speed and accuracy of these tests may not meet the current demand; thus, alternative technology platforms are being developed. Nano biosensor technology platforms have been established as a promising diagnostic tool for rapid and accurate detection of viruses as well as other life-threatening diseases even in resource-limited settings. This review aims to provide a short overview of recent advancements in molecular and biosensor-based diagnosis of viruses, including the human coronaviruses, and highlight the challenges and future perspectives of these detection technologies.
Keywords: Biosensors; COVID-19; Coronavirus; MERS-CoV; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
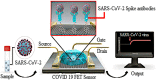
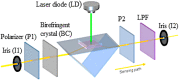
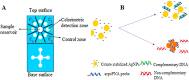
References
-
- Henry R. Etymologia: coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020;26(5):1027.
-
- Gao Y., Yan L., Huang Y., Liu F., Zhao Y., Cao L., Wang T., Sun Q., Ming Z., Zhang L., Ge J., Zheng L., Zhang Y., Wang H., Zhu Y., Zhu C., Hu T., Hua T., Zhang B., Yang X., Li J., Yang H., Liu Z., Xu W., Guddat L.W., Wang Q., Lou Z., Rao Z. Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science. 2020;368(6492):779–782. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

