Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children
- PMID: 32911567
- PMCID: PMC8479592
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009185.pub3
Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children
Abstract
Background: In children with urinary tract infection (UTI), only those with pyelonephritis (and not cystitis) are at risk for developing long-term renal sequelae. If non-invasive biomarkers could accurately differentiate children with cystitis from children with pyelonephritis, treatment and follow-up could potentially be individualized. This is an update of a review first published in 2015.
Objectives: The objectives of this review were to 1) determine whether procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can replace the acute DMSA scan in the diagnostic evaluation of children with UTI; 2) assess the influence of patient and study characteristics on the diagnostic accuracy of these tests, and 3) compare the performance of the three tests to each other.
Search methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, DARE, Web of Science, and BIOSIS Previews through to 17th December 2019 for this review. The reference lists of all included articles and relevant systematic reviews were searched to identify additional studies not found through the electronic search.
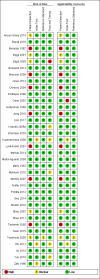
Selection criteria: We only considered published studies that evaluated the results of an index test (PCT, CRP, ESR) against the results of an acute-phase 99Tc-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan (conducted within 30 days of the UTI) in children aged 0 to 18 years with a culture-confirmed episode of UTI. The following cut-off values were used for the primary analysis: 0.5 ng/mL for procalcitonin, 20 mg/L for CRP and 30 mm/hour for ESR.
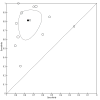
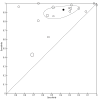
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently applied the selection criteria to all citations and independently abstracted data. We used the bivariate model to calculate pooled random-effects pooled sensitivity and specificity values.
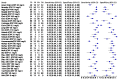
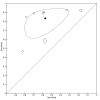
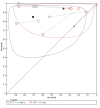
Main results: A total of 36 studies met our inclusion criteria. Twenty-five studies provided data for the primary analysis: 12 studies (1000 children) included data on PCT, 16 studies (1895 children) included data on CRP, and eight studies (1910 children) included data on ESR (some studies had data on more than one test). The summary sensitivity estimates (95% CI) for the PCT, CRP, ESR tests at the aforementioned cut-offs were 0.81 (0.67 to 0.90), 0.93 (0.86 to 0.96), and 0.83 (0.71 to 0.91), respectively. The summary specificity values for PCT, CRP, and ESR tests at these cut-offs were 0.76 (0.66 to 0.84), 0.37 (0.24 to 0.53), and 0.57 (0.41 to 0.72), respectively.
Authors' conclusions: The ESR test does not appear to be sufficiently accurate to be helpful in differentiating children with cystitis from children with pyelonephritis. A low CRP value (< 20 mg/L) appears to be somewhat useful in ruling out pyelonephritis (decreasing the probability of pyelonephritis to < 20%), but unexplained heterogeneity in the data prevents us from making recommendations at this time. The procalcitonin test seems better suited for ruling in pyelonephritis, but the limited number of studies and the marked heterogeneity between studies prevents us from reaching definitive conclusions. Thus, at present, we do not find any compelling evidence to recommend the routine use of any of these tests in clinical practice.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Kai J Shaikh: none known
Victor A Osio: none known
Nader Shaikh: none known
Mariska MG Leeflang: none known
Figures





Update of
-
Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 20;1(1):CD009185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009185.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 10;9:CD009185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009185.pub3. PMID: 25603480 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ansari Gilani 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ansari Gilani K, Modaresi Esfeh J, Gholamrezanezhad A, Gholami A, Mamishi S, Eftekhari M, et al. Predictors of abnormal renal cortical scintigraphy in children with first urinary tract infection: the importance of time factor. International Urology & Nephrology 2010;42(4):1041-7. [MEDLINE: ] [2819452] - PubMed
Barati 2016 {published data only}
Benador 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Benador D, Benador N, Slosman D, Mermillod B, Girardin E. Are younger children at highest risk of renal sequelae after pyelonephritis? Lancet 1997;349(9044):17-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Girardin E, Benador N, Gendrel D, Greder C, Benador D, Bohuon C, et al. Procalcitonin is a marker of severity of renal lesions in pyelonephritis [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;9(Program & Abstracts Issue):125A. [BIOSIS Previews: PREV199800022706] - PubMed
Biggi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Biggi A, Dardanelli L, Pomero G, Cussino P, Noello C, Sernia O, et al. Acute renal cortical scintigraphy in children with a first urinary tract infection. Pediatric Nephrology 2001;16(9):733-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bigot 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bigot S, Leblond P, Foucher C, Hue V, D'Herbomez M, Foulard M. Usefulness of procalcitonin for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children [Apport du dosage de la procalcitonine pour le diagnostic de pyélonéphrite aiguë de l'enfant]. Archives de Pédiatrie 2005;12(7):1075-80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bouguila 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bouguila J, Khalef I, Charfeddine B, Ben Rejeb M, Chatti K, Limam K et al. Comparative study of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in the severity diagnosis of pyelonephritis in children [Etude comparative de la proteine C-reactive et de la procalcitonine dans lediagnostic de severite des pyelonephrites aigues de l’enfant]. Pathologie Biologie 2013;61(3):93-98. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bressan 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bressan S, Andreola B, Zucchetta P, Montini G, Burei M, Perilongo G, et al. Procalcitonin as a predictor of renal scarring in infants and young children. Pediatric Nephrology 2009;24(6):1199-204. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Chen SM, Chang HM, Hung TW, Chao YH, Tsai JD, Lue KH, et al. Diagnostic performance of procalcitonin for hospitalised children with acute pyelonephritis presenting to the paediatric emergency department. Emergency Medicine Journal 2013;30(5):406-410. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Donoso 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Donoso G, Lobo G, Arnello F, Arteaga MP, Hevia P, Rosati P, et al. Tc 99M DMSA scintigraphy in children with a first episode of acute pyelonephritis: correlation with laboratory tests, echography and the presence of vesico-ureteral reflux [Cintigrama renal DMSA en ninos con primera pielonefritis aguda: correlacion con examenes de laboratorio, ecografia y la presencia de reflujo vesico ureteral]. Revista Medica de Chile 2004;132(1):58-64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fretzayas 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fretzayas A, Moustaki M, Gourgiotis D, Bossios A, Koukoutsakis P, Stavrinadis C. Polymorphonuclear elastase as a diagnostic marker of acute pyelonephritis in children. Pediatrics 2000;105(2):E28. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Garin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Garin EH, Olavarria F, Araya C, Broussain M, Barrera C, Young L. Diagnostic significance of clinical and laboratory findings to localize site of urinary infection. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(7):1002-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hoberman 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hoberman A, Wald ER, Hickey RW, Baskin M, Charron M, Majd M, et al. Oral versus initial intravenous therapy for urinary tract infections in young febrile children. Pediatrics 1999;104(1 Pt 1):79-86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jung 2016 {published data only}
Kim 2017 {published data only}
-
- Kim BK, Yim HE, Yoo KH. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a marker of acute pyelonephritis in children. Pediatric Nephrology 2017;32(3):477-84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kotoula 2009a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kotoula A, Gardikis S, Tsalkidis A, Mantadakis E, Zisimopoulos A, Deftereos S, et al. Comparison of serum procalcitonin and commonly used inflammatory markers for the early prediction of acute pyelonephritis in children [abstract]. European Urology Supplements 2008;7(3):247. [DOI: 10.1016/S1569-9056(08)60704-6] [Biosis Previews: PREV200800283210] - DOI
-
- Kotoula A, Gardikis S, Tsalkidis A, Mantadakis E, Zissimopoulos A, Deftereos S, et al. Comparative efficacies of procalcitonin and conventional inflammatory markers for prediction of renal parenchymal inflammation in pediatric first urinary tract infection. Urology 2009;73(4):782-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kotoula A, Gardikis S, Tsalkidis A, Mantadakis E, Zissimopoulos A, Kambouri, K, et al. Procalcitonin for the early prediction of renal parenchymal involvement in children with UTI: preliminary results. International Urology & Nephrology 2009;41(2):393-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Krzemien 2019 {published data only}
-
- Krzemien G, Panczyk-Tomaszewska M, Kotula I, Demkow U, Szmigielska A. Diagnostic accuracy of urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and urine kidney injury molecule-1 as predictors of acute pyelonephritis in young children with febrile urinary tract infection. Central-European Journal of Immunology 2019;44(2):174-80. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Kuzmanovska 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kuzmanovska D, Sahpazova E, Bogdanovska A, Konstadinova R. Parenchymal renal damage in children with urinary tract infection [Parenhimna bubrezna ostecenja u djece sa infekcijom mokracnog sustava]. Paediatria Croatica, Supplement 2008;52(1):212-7. [EMBASE: 351830973]
Levtchenko 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Levtchenko E, Lahy C, Levy J, Ham H, Piepsz A. Treatment of children with acute pyelonephritis: a prospective randomized study. Pediatric Nephrology 2001;16(11):878-84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Levtchenko EN, Lahy C, Levy J, Ham HR, Piepsz A. Role of Tc-99m DMSA scintigraphy in the diagnosis of culture negative pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 2001;16(6):503-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mahyar 2014 {published data only}
-
- Mahyar A, Ayazi P, Ahmadi R, Daneshi-Kohan MM, Hashemi HJ, Dalirani R, et al. Are serum procalcitonin and interleukin-1 beta suitable markers for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children? Prague Medical Report 2014;115(1-2):16-23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Martin Aguado 2000 {published data only}
-
- Martín Aguado MJ, Canals Baeza A, Vioque López J, Tarazona JL, Flores Serrano J. Technetium-99m-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scintigraphy in the first febrile urinary tract infection in children [Gammagrafía con tecnecio-99m-ácido dimercaptosuccínico en el estudio de la primera infección urinaria febril del niño]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 2000;52(1):23-30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Melis 1992 {published data only}
-
- Melis K, Vandevivere J, Hoskens C, Vervaet A, Sand A, Van Acker KJ. Involvement of the renal parenchyma in acute urinary tract infection: the contribution of 99mTc dimercaptosuccinic acid scan. European Journal of Pediatrics 1992;151(7):536-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mohkam 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mohkam M, Maham S, Rahmani A, Naghi I, Otokesh B, Raiiati H, et al. Technetium Tc 99m dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scintigraphy in children with acute pyelonephritis: correlation with other imaging tests. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2010;4(4):297-301. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Montini 2007 {published and unpublished data}
Nikfar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nikfar R, Khotaee G, Ataee N, Shams S. Usefulness of procalcitonin rapid test for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children in the emergency department. Pediatrics International 2010;52(2):196-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Printza 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Printza N, Farmaki E, Piretzi K, Arsos G, Kollios K, Papachristou F. Acute phase 99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in infants with first episode of febrile urinary tract infection. World Journal of Pediatrics 2012;8(1):52-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Seo 2014 {published data only}
-
- Seo WH, Nam SW, Lee EH, Je BK, Yim HE, Choi BM. A rapid plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin assay for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in infants with acute febrile urinary tract infections: a preliminary study. European Journal of Pediatrics 2014;173(2):229-32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shaikh 2019 {published data only}
Sheu 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sheu JN, Chen MC, Cheng SL, Lee IC, Chen SM, Tsay GJ. Urine interleukin-1beta in children with acute pyelonephritis and renal scarring. Nephrology 2007;12(5):487-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Sheu JN, Chen MC, Lue KH, Cheng SL, Lee IC, Chen SM, et al. Serum and urine levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in children with acute pyelonephritis. Cytokine 2006;36(5-6):276-82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sheu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sheu JN, Chang HM, Chen SM, Hung TW, Lue KH. The role of procalcitonin for acute pyelonephritis and subsequent renal scarring in infants and young children. Journal of Urology 2011;186(5):2002-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Taskinen 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Taskinen S, Ronnholm K. Post-pyelonephritic renal scars are not associated with vesicoureteral reflux in children. Journal of Urology 2005;173(4):1345-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tekin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Tekin M, Konca C, Gulyuz A, Uckardes F, Turgut M. Is the mean platelet volume a predictive marker for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children? Clinical & Experimental Nephrology 2015;19(4):688-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tuerlinckx 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tuerlinckx D, Vander Borght T, Glupczynski Y, Galanti L, Roelants V, Krug B, et al. Is procalcitonin a good marker of renal lesion in febrile urinary tract infection? European Journal of Pediatrics 2005;164(10):651-2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wu JH, Chiou YH, Chang JT, Wang HP, Chen YY, Hsieh KS. Urinary tract infection in infants: a single-center clinical analysis in Southern Taiwan. Pediatrics & Neonatology 2012;53(5):283-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xu 2014 {published data only}
Yun 2018 {published data only}
Zaki 1996 {published data only}
-
- Zaki M, Al Mutari G, Al Saleh Q, Ramadan DG. Febrile urinary tract infection in children: role of 99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan and other imaging techniques. Annals of Saudi Medicine 1996;16(4):410-3. [EMBASE: 1996271418] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agrawal 2013 {published data only}
-
- Agrawal P, Pandey A, Sompura S, Pursnani ML. Role of blood C - reactive protein levels in upper urinary tract infection and lower urinary tract infection in adult patients (>16 years). Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 2013;61(7):462-3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Al Kholi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Al Kholi UM, Mostafa M, Gaballa A. The role of urinary interleukin-8 level in diagnosis and differentiation between different types of urinary tract infection in children. Current Urology 2010;4(4):203-7. [EMBASE: 2010698409]
Andersson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Andersson L, Preda I, Hahn-Zoric M, Hanson LA, Jodal U, Sixt R, et al. Urinary proteins in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatric Nephrology 2009;24(8):1533-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Andreola 2007 {published data only}
-
- Andreola B, Bressan S, Callegaro S, Liverani A, Plebani M, Da Dalt, L. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as diagnostic markers of severe bacterial infections in febrile infants and children in the emergency department. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2007;26(8):672-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Arambasic 2016 {published data only}
-
- Arambasic J, Mandic S, Debeljak Z, Mandic D, Horvat V, Seric V. Differentiation of acute pyelonephritis from other febrile states in children using urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL). Clinical Chemistry & Laboratory Medicine 2016;54(1):55-61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Asom 1996 {published data only}
-
- Asom AA, Bardfeld PA, Kaskel FJ, Katz SP. Clinical value of renal cortical scintigraphy (RCS) in localizing urinary tract infections (UTI) in adolescent females [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(9):616.
Ataei 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ataei N, Safaian B, Madani A, Esfahani ST, Ataei F. Renal parenchymal changes in children with acute pyelonephritis using DMSA scan and the relationship with certain biologic factors. Tehran University Medical Journal 2009;67(2):125-31. [EMBASE: 2009456653]
Ayazi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ayazi P, Mahyar A, Hashemi HJ, Daneshi MM, Karimzadeh T, Salimi F. Comparison of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein tests in children with urinary tract infection. Iranian Journal of Pediatrics 2009;19(4):381-6. [EMBASE: 2010034009]
Ayazi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ayazi P, Mahyar A, Daneshi MM, Hashemi HJ, Pirouzi M, Esmailzadehha N. Diagnostic accuracy of the quantitative C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and white blood cell count in urinary tract infections among infants and children. Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences 2013;20(5):40-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Azab 2016 {published data only}
Banuelos‐Andrio 2017 {published data only}
-
- Banuelos-Andrio L, Espino-Hernandez M, Ruperez-Lucas M, Villar-Del Campo MC, Romero-Carrasco CI, Rodriguez-Caravaca G. Usefulness of analytical parameters in the management of paediatric patients with suspicion of acute pyelonephritis. Is procalcitonin reliable? Revista Espanola de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular 2017;36(1):2-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Belhadj‐Tahar 2008 {published data only}
Benador 1994 {published data only}
-
- Benador D, Benador N, Slosman DO, Nussle D, Mermillod B, Girardin E. Cortical scintigraphy in the evaluation of renal parenchymal changes in children with pyelonephritis. Journal of Pediatrics 1994;124(1):17-20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Benador 1998 {published data only}
-
- Benador N, Siegrist C, Gendrel D, Greder C, Benador D, Assicot M, et al. Procalcitonin is a marker of severity of renal lesions in pyelonephritis. Pediatrics 1998;102(6):1422-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Benador 2001 {published data only}
Benigno 1986 {published data only}
-
- Benigno V, Di Peri S, Distefano F, Como G, Boncori R. Laboratory parameters as a guide for the radiologic study of infections of the urinary tract in childhood [I parametri di laboratorio come guida allo studio radiologico delle infezioni delle vie urinarie in eta pediatrica]. Pediatria Medica e Chirurgica 1986;8(1):91-3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bouissou 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bouissou F, Belmonte D, Danet B, Baunin C, Raynaud N, Salles JP, et al. Value of DMSA renal scintigraphy in acute pyelonephritis in pediatric patients [Interet de la scintigraphie renale au DMSA dans les pyelonephritis aigues de l'enfant]. Annales de Pediatrie 1994;41(1):7-13. [EMBASE: 1994068022]
Bouissou 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bouissou F, Munzer C, Decramer S, Roussel B, Novo R, Morin D, et al. Prospective, randomized trial comparing short and long intravenous antibiotic treatment of acute pyelonephritis in children: dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphic evaluation at 9 months. Pediatrics 2008;121(3):e553-60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brouhard 1997 {published data only}
-
- Brouhard BH. Early (99m)Tc dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scintigraphy in symptomatic first-time urinary tract infection. Clinical Pediatrics 1997;36(6):366-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Buyan 1993 {published data only}
-
- Buyan N, Bircan ZE, Hasanoglu E, Ozturk E, Bayhan H, Rota S. The importance of 99mTc DMSA scanning in the localization of childhood urinary tract infections. International Urology & Nephrology 1993;25(1):11-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Capdevila 2001 {published data only}
-
- Capdevila Cogul E, Martin Ibanez I, Mainou Cid C, Toral Rodriguez E, Cols Roig Mf, Agut Quijano T, et al. First urinary tract infection in healthy infants: epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment [Primera infeccion urinaria en el lactante sano: epidemiologia y pautas de diagnostico y tratamiento]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 2001;55(4):310-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Castello 1995 {published data only}
-
- Castello Girona F, Vilaplana Canto E, Yeste Fernandez D, Roca Bielsa I, Enriquez Civico G. 99mTc dimercaptosuccinic scan in the study of the first urinary tract infection in infants [Gamamarafia con 99mTecnecio-acido dimercaptosuccinico en el estudio de la primera infeccion urinaria del lactante]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1995;42(2):118-22. [EMBASE: 1995091284]
Chiou 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chiou YY, Chen MJ, Chiu NT, Lin CY, Tseng CC. Bacterial virulence factors are associated with occurrence of acute pyelonephritis but not renal scarring. Journal of Urology 2010;184(5):2098-102. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Christian 2000 {published data only}
Connell 1993 {published data only}
-
- Connell H, Man P, Jodal U, Lincoln K, Svanborg C. Lack of association between hemolysin production and acute inflammation in human urinary tract infection. Microbial Pathogenesis 1993;14(6):463-72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Craig 1998 {published data only}
-
- Craig JC, Irwig LM, Knight JF, Sureshkumar P, Roy L. Symptomatic urinary tract infection in preschool Australian children. Journal of Paediatrics & Child Health 1998;34(2):154-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
de Man 1988 {published data only}
-
- Man P, Jodal U, Lincoln K, Eden CS. Bacterial attachment and inflammation in the urinary tract. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988;158(1):29-35. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Doganis 2007 {published data only}
-
- Doganis D, Siafas K, Mavrikou M, Issaris G, Martirosova A, Perperidis G, et al. Does early treatment of urinary tract infection prevent renal damage? Pediatrics 2007;120(4):e922-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dura Trave 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dura Trave T, Gonzalez Montero R, Juste Ruiz M, Gonzalez de Dios J, Carratala Marco F, Moya Benavent M, et al. Usefulness of renal scintigraphy in the assessment of the first febrile urinary infection in children [Utilidad de la gammagrafia renal en la valoracion de la primera infeccion urinaria febril en la edad pediatrica]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1997;47(4):378-82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ehsanipour 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ehsanipour F, Noorbakhsh S, Zarabi V, Movahedi Z, Rahimzadeh N. Comparison the serum STREM1 levels between children with upper and lower UTI. Current Pediatric Review 2017;13(2):152-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Elo 1985 {published data only}
-
- Elo J, Tallgren LG, Vaisanen V, Korhonen TK, Svenson SB, Makela PH. Association of P and other fimbriae with clinical pyelonephritis in children. Scandinavian Journal of Urology & Nephrology 1985;19(4):281-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eremeeva 2016 {published data only}
-
- Eremeeva A, Dlin V, Korsunsky A, Orekhova S, Bondarenko E, Gurbanova S. Lipocalin-2 associated with neutrophilic gelatinases (uNGAL) as the marker of microbial inflammatory diseases of kidneys and urinary tract in children [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2016;31(10):1767-8. [EMBASE: 612479409]
Fang 2017 {published data only}
Fang 2020 {published data only}
-
- Fang C, Wang Z, Dai Y, Chang W, Sun L, Ma X. Serum human neutrophil lipocalin: An effective biomarker for diagnosing bacterial infections. Clinical Biochemistry 2020;75:23-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fernandez 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez Lopez A, Luaces Cubells C, Valls Tolosa C, Ortega Rodriguez J, Garcia Garcia J J, Mira Vallet A, et al. Procalcitonin in the early diagnosis of invasive bacterial infection in febrile infants [Procalcitonina para el diagnostico precoz de infeccion bacteriana invasiva en el lactante febril]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 2001;55(4):321-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fernandez 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez Lopez A, Luaces Cubells C, Garcia Garcia JJ, Fernandez Pou J, Spanish Society of Pediatric Emergencies. Procalcitonin in pediatric emergency departments for the early diagnosis of invasive bacterial infections in febrile infants: results of a multicenter study and utility of a rapid qualitative test for this marker. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2003;22(10):895-903. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fernandez‐Menendez 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez-Menendez JM, Malaga S, Matesanz JL, Solis G, Alonso S, Perez-Mendez C. Risk factors in the development of early technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scintigraphy lesions during first urinary tract infection in children. Acta Paediatrica 2003;92(1):21-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Figueiredo 1999 {published data only}
-
- Figueiredo S, Rocha P, Coelho E, Alexandrino AM, Rocha H. Retrospective study of urinary tract infection in infants [Estudo retrospectivo de infeccao urinaria alta em lactentes]. Nascer e Crescer 1999;8(2):89-92. [EMBASE: 1999270461]
Friedman‐Gruszczynska 2008 {published data only}
-
- Friedman-Gruszczynska J. Assessment of clinical relevance of CRP levels in infectious diseases in children [Ocena przydatnosci klinicznej oznaczania stezenia bialka CRP w chorobach infekcyjnych u dziec]. Pediatria Polska 2008;83(1):49-53. [EMBASE: 2008097172]
Galetto‐Lacour 2002 {published data only}
-
- Galetto-Lacour A, Zamora S, Gervaix A. Blood markers of severe bacterial infections [abstract]. In: 42nd Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; Sep 27-30 2002; San Diego, USA. 2002.
Galetto‐Lacour 2003 {published data only}
-
- Galetto-Lacour A, Zamora SA, Gervaix A. Bedside procalcitonin and C-reactive protein tests in children with fever without localizing signs of infection seen in a referral center. Pediatrics 2003;112(5):1054-60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Garcia de Guadiana 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Garcia de Guadiana L, Gonzalez J, Gonzalez M, Martin E, Albaladejo M, Cortes P. Usefulness of C-reactive protein in admission to localize site of urinary infection in children [abstract]. Clinical Chemistry & Laboratory Medicine 2011;49(Suppl 1):S637. [EMBASE: 70517512]
Gendrel 1998 {published data only}
-
- Gendrel D. Urinary tract infection and biological markers: C-reactive protein, interleukins and procalcitonin [Infection urinaire biologiques: proteine C reactive, interleukine et procalcitonine]. Archives de Pediatrie 1998;5 Suppl 3:269-73S. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gervaix 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gervaix A, Galetto-Lacour A, Gueron T, Vadas L, Zamora S, Suter S, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein rapid tests for the management of children with urinary tract infection. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2001;20(5):507-11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ghasemi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ghasemi K, Montazeri S, Pashazadeh AM, Javadi H, Assadi M. Correlation of 99mTc-DMSA scan with radiological and laboratory examinations in childhood acute pyelonephritis: a time-series study [abstract]. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging 2013;40(Suppl 2):S279. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Ghasemi 2016 {published data only}
Girardin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Girardin E. Pyelonephritis in children: new tools for evaluation [Pyelonephrites de l'enfant: nouveaux moyens d'evaluation]. Medecine Therapeutique Pediatrie 2000;3(5):376-80. [EMBASE: 30944096]
Giunta 2014 {published data only}
-
- Giunta F, Forfori F, Seri G. Molecular markers for urinary tract infections. Official Gazette of the United States Patent & Trademark Office Patents 2014. [US Patent US 2013/0084650 A1 ]
Grouteau 1999 {published data only}
-
- Grouteau E, Fauvel J, Blum G, Ouhayoun E, Salles J, Decramer S, et al. Phospholipase A2 (Pla2) and C reactive protein (CRP) in acute pyelonephritis in children. Correlation with DMSA scan [abstract no: P92]. Pediatric Nephrology 1999;13.
Guermazi 1993 {published data only}
-
- Guermazi F, Lenoir P, Verboven M, Smets A, Braeckman J, Jonckheer M, et al. Technetium 99m labeled dimercaptosuccinic acid (99m Tc-DMSA) scintigraphy in the diagnosis and follow-up of urinary infections in children [Apport de la scintigraphie a l'acide dimercaptosuccinque marque au technetium 99m (99mTC-DSA) dans le diagnostic et le suivi des infections urinaires de l'enfant]. Archives Francaises de Pediatrie 1993;50(5):391-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gurgoze 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gurgoze M, Akarsu S, Yilmaz E, Godekmerdan A, Akca Z, Ciftci I, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and procalcitonin in children with acute pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 2005;20(10):1445-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Guven 2006 {published data only}
-
- Guven AG, Kazdal HZ, Koyun M, Aydn F, Gungor F, Akman S, et al. Accurate diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis: How helpful is procalcitonin? Nuclear Medicine Communications 2006;27(9):715-21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hahn 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hahn H, Moon DH, Yang YJ, Park YS. Renal scarring after acute pyelonephritis in children under the age of 5 years is primarily related to the extent and severity of acute inflammatory changes [abstract]. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2003;44(5 Suppl):358. [BIOSIS Previews: PREV200300383499]
Han 2016 {published data only}
Hellerstein 1981 {published data only}
-
- Hellerstein S, Duggan E, Welchert E, Mansour F. Localization of the site or urinary tract infections using serum C reactive protein [abstract]. Pediatric Research 1981;15(4 Pt 2):694. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-198104001-01528] [BIOSIS Previews: PREV198121026875] - DOI
Hellerstein 1982 {published data only}
-
- Hellerstein S, Duggan E, Welchert E, Mansour F. Serum C-reactive protein and the site of urinary tract infections. Journal of Pediatrics 1982;100(1):21-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hewitt 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hewitt IK, Zucchetta P, Rigon L, Maschio F, Molinari PP, Tomasi L, et al. Early treatment of acute pyelonephritis in children fails to reduce renal scarring: data from the Italian Renal Infection Study Trials. Pediatrics 2008;122(3):486-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hitzel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hitzel A, Liard A, Vera P, Manrique A, Menard JF, Dacher JN. Color and power Doppler sonography versus DMSA scintigraphy in acute pyelonephritis and in prediction of renal scarring. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2002;43(1):27-32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hsu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Hsu CC, Tsai JD, Ku MS, Chen SM, Liao PF, Hung TW, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and diagnostic imaging in infants younger than 2 months old hospitalized with a first febrile urinary tract infection: a population-based comparative study. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2016;35(8):840-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Huang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Huang DT, Huang FY, Tsai TC, Tsai JD, Chiu NC, Lin CC. Clinical differentiation of acute pyelonephritis from lower urinary tract infection in children. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology & Infection 2007;40(6):513-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hubert‐Dibon 2018 {published data only}
-
- Hubert-Dibon G, Danjou L, Feildel-Fournial C, Vrignaud B, Masson D, Launay E, et al. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein may help to detect invasive bacterial infections in children who have fever without source. Acta Paediatrica 2018;107(7):1262-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ilyas 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ilyas M, Mastin ST, Richard GA. Age-related radiological imaging in children with acute pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 2002;17(1):30-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jakobsson 1992a {published data only}
Jakobsson 1992b {published data only}
-
- Jakobsson B, Nolstedt L, Svensson L, Soderlundh S, Berg U. 99mTechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children: relation to clinical and radiological findings. Pediatric Nephrology 1992;6(4):328-34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jakobsson 1994 {published data only}
Jakobsson 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jakobsson B, Svensson L. Transient pyelonephritic changes on 99mTechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan for at least five months after infection. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86(8):806-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jaksic 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jaksic E, Bogdanovic R, Artiko V, Saranovic DS, Petrasinovic Z, Petrovic M, et al. Diagnostic role of initial renal cortical scintigraphy in children with the first episode of acute pyelonephritis. Annals of Nuclear Medicine 2011;25(1):37-43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jantausch 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jantausch BA, Rifai N, Getson P, Akram S, Majd M, Wiedermann BL. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase and beta-2-microglobulin in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection in febrile infants. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1994;13(4):294-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jodal 1975 {published data only}
-
- Jodal U, Lindberg U, Lincoln K. Level diagnosis of symptomatic urinary tract infections in childhood. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1975;64(2):201-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johnson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Johnson CE, Shurin PA, Marchant CD, Strieter CM, Murdell-Panek D, Debaz BP, et al. Identification of children requiring radiologic evaluation for urinary infection. Pediatric Infectious Disease 1985;46(6):656-63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kanellopoulos 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kanellopoulos TA, Vassilakos PJ, Kantzis M, Ellina A, Kolonitsiou F, Papanastasiou DA. Low bacterial count urinary tract infections in infants and young children. European Journal of Pediatrics 2005;164(6):355-61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kangari 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kangari G, Esteghamati M, Ghasemi K, Mahboobi H. Predictive accuracy of urinary beta2-microglobulin for kidney injury in children with acute pyelonephritis. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2015;9(1):19-24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Karakatsani 1997 {published data only}
-
- Karakatsani Z, Kipuru C, Stefanidis C. Is C-reactive protein reliable for the prediction of renal lesions in infants with urinary tract infection (UTI)? [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 1997;11(5):C56. [BIOSIS Previews: PREV199799837360]
Karavanaki 2007 {published data only}
-
- Karavanaki K, Angelos Haliotis F, Sourani M, Kariyiannis C, Hantzi E, Zachariadou L, et al. DMSA scintigraphy in febrile urinary tract infections could be omitted in children with low procalcitonin levels. Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice 2007;15(6):377-81. [EMBASE: 350135450]
Kassir 2001 {published data only}
Katz 1993 {published data only}
-
- Katz SP, Barfeld PA, Kaskel FJ. Clinical value of DMSA scan in differentiating acute pyelonephritis (APN) from other urinary tract infections (UTI) in adolescent females [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1993;4.
Katz 2002 {published data only}
-
- Katz SP, Gromisch DS, Balbi HJ, Vilela MG, Constantatos C, Affan AA. A seven year retrospective review of patients diagnosed with urinary tract infection (UTI) from birth to twenty-four months of age [abstract]. Pediatric Research 2002;51.
Kiker 1982 {published data only}
-
- Kiker JD, Woodside JR, Reed WP, Borden TA, Woodside MD. Urinary lactic dehydrogenase and serum C-reactive protein as means of localizing the site of urinary tract infection in patients with ileal conduits. Journal of Urology 1982;128(4):749-51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kilicaslan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kilicaslan B, Alp H, Yildirim M, Inandi T. Diagnostic value of MAG3 scintigraphy and DMSA scintigraphy in renal parenchyma damage and acute pyelonephritis of children. Cukurova Medical Journal 2016;41(3):464-471. [DOI: 10.17826/cukmedj.237484] - DOI
Kilicaslan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kilicaslan B, Noyan A, Cengiz N, Sariturk C, Parmaksiz G, Baskin E. Can we differentiate pyelonephritis and cystitis without 99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in children? Cukurova Medical Journal 2015;40(3):495-503. [DOI: ]
Kim 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kim S, Kim I, Kim E, Yoo I, Chung Y, Sohn H, et al. Planar and pinhole renal cortical scintigraphic findings correlated to consolidated clinical parameters in acute urinary tract infection [abstract]. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2001;42.
Koufadaki 2014 {published data only}
-
- Koufadaki AM, Karavanaki KA, Soldatou A, Tsentidis Ch, Sourani MP, Sdogou T, et al. Clinical and laboratory indices of severe renal lesions in children with febrile urinary tract infection. Acta Paediatrica 2014;103(9):e404-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Krzemien 2004 {published data only}
-
- Krzemien G, Roszkowska-Blaim M, Kostro I, Szmigielska A, Karpinska M, Sieniawska M, et al. Urinary levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in children with urinary tract infections to age 2. Medical Science Monitor 2004;10(11):CR593-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Krzemien 2016 {published data only}
Krzemien 2017 {published data only}
-
- Krzemien G, Panczyk-Tomaszewska M, Adamczuk D, Kotula I, Demkow U, Szmigielska A. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a biomarker for early diagnosis of urinary tract infections in infants. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology 2018;1047:71-80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kupperman 2019 {published data only}
Lai 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lai SW, Ng KC. Retrospective analysis of inflammatory parameters in acute pyelonephritis. Scandinavian Journal of Urology & Nephrology 2003;37(3):250-2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lee JH, Son CH, Lee MS, Park YS. Vesicoureteral reflux increases the risk of renal scars: a study of unilateral reflux. Pediatric Nephrology 2006;21(9):1281-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lee HY, Soh BH, Hong CH, Kim MJ, Han SW. The efficacy of ultrasound and dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in predicting vesicoureteral reflux in children below the age of 2 years with their first febrile urinary tract infection. Pediatric Nephrology 2009;24(10):2009-13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2015 {published data only}
Lee 2017 {published data only}
Lee 2017a {published data only}
-
- Lee JW, Park JS, Park KB, Yoo GH, Kim SS, Lee SM. Prediction of renal cortical defect and scar using neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in children with febrile urinary tract infection. Nuklear-Medizin 2017;56(3):109-14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2018 {published data only}
-
- Lee JW, Her SM, Kim JH, Lee KH, Eisenhut M, Park SJ, et al. D-dimer as a marker of acute pyelonephritis in infants younger than 24 months with urinary tract infection. Pediatric Nephrology 2018;33(4):631-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2018a {published data only}
Lee 2018b {published data only}
Lee 2019 {published data only}
-
- Lee JH. Discrimination of culture negative pyelonephritis in children with suspected febrile urinary tract infection and negative urine culture results. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology & Infection 2019;52(4):598-603. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Leroy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Leroy S, Fernandez-Lopez A, Nikfar R, Romanello C, Bouissou F, Gervaix A, et al. Procalcitonin predicts well acute pyelonephritis and renal scars in children with urinary tract infection [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2012;27(Suppl 2):ii547.
Levine 2018 {published data only}
-
- Levine AR, Tran M, Shepherd J, Naut E. Utility of initial procalcitonin values to predict urinary tract infection. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2018;36(11):1993-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lin DS, Huang SH, Lin CC, Tung YC, Huang TT, Chiu NC, et al. Urinary tract infection in febrile infants younger than eight weeks of age. Pediatrics 2000;105(2):E20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Linne 1994 {published data only}
-
- Linne T, Fituri O, Escobar-Billing R, Karlsson A, Wikstad I, Aperia A, et al. Functional parameters and 99mtechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in acute pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 1994;8(6):694-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lomberg 1992 {published data only}
-
- Lomberg H, Jodal U, Leffler H, De Man P, Svanborg C. Blood group non-secretors have an increased inflammatory response to urinary tract infection. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1992;24(1):77-83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lucas‐Saez 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lucas-Saez E, Ferrando-Monleon S, Marin-Serra J, Bou-Monterde R, Fons-Moreno J, Peris-Vidal A, et al. Predictive factors for kidney damage in febrile urinary tract infection. Usefulness of procalcitonin. Nefrologia 2014;34(4):451-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mahyar 2013 {published data only}
Majd 1991 {published data only}
-
- Majd M, Rushton HG, Jantausch B, Wiedermann BL. Relationship among vesicoureteral reflux, P-fimbriated Escherichia coli, and acute pyelonephritis in children with febrile urinary tract infection. Journal of Pediatrics 1991;119(4):578-85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Majd 1992 {published data only}
-
- Majd M, Rushton HG. Renal cortical scintigraphy in the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis. Seminars in Nuclear Medicine 1992;22(2):98-111. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Malaga 1978 {published data only}
-
- Malaga S, Matesanz JL, Dieguez MA, Crespo M. Value of the C reactive protein, urinary lactic dehydrogenase and renal capacity of concentration in the topographic diagnosis of the urinary infection in infancy (author's transl) [Valor de la proteina C reactiva, lactilo-dehidrogenasa urinaria y capacidad renal de concentracion en el diagnostico topografico de la infeccion urinaria en la infancia]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1978;11(6-7):485-96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Masajtis‐Zagajewska 2015 {published data only}
Mazigh Mrad 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mazigh Mrad S, Fetni I, Rabeh O, Oubich F, Boukthir S, Barsaoui S. Contribution of clinical, biological and radiological parameters in the diagnosis of urinary infection localization [Apport des parametres cliniques biologiques et radiogiques dans le diagnostic de localisation de l'infection urinaire]. Tunisie Medicale 2002;80(10):28-32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mohkam 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mohkam M, Karimi A, Karimi H, Sharifian M, Armin S, Dalirani R, et al. Urinary interleukin-8 in acute pyelonephritis of children: a before-after study. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2008;2(4):193-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moldovan 2015 {published data only}
Montini 2008 {published data only}
-
- Montini G, Rigon L, Zucchetta P, Fregonese F, Toffolo A, Gobber D, et al. Prophylaxis after first febrile urinary tract infection in children? A multicenter, randomized, controlled, noninferiority trial. Pediatrics 2008;122(5):1064-71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Montini 2009 {published data only}
-
- Montini G, Zucchetta P, Tomasi L, Talenti E, Rigamonti W, Picco G, et al. Value of imaging studies after a first febrile urinary tract infection in young children: data from Italian renal infection study 1. Pediatrics 2009;123(2):e239-46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moon 2009 {published data only}
-
- Moon DG, Oh MM, Nam SG, Jin MH, Park HS, Cheon J, et al. Predictive factors for acute scintingraphic lesion and ultimate scar formation in patients with acute febrile UTI [abstract]. Journal of Urology 2009;181(4 Suppl 1):380. [EMBASE: 70113158]
Mussap 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mussap M, Cataldi L, Plebani M, Fanos V. Laboratory investigation for the early diagnosis and monitoring of neonatal urinary tract infections: The present situation and future perspectives. Journal of Chemotherapy 2006;18 Spec no 3:9-13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Naseri 2008 {published data only}
-
- Naseri M. Alterations of peripheral leukocyte count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein in febrile urinary tract infection. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2008;2(3):137-42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Naseri 2017 {published data only}
-
- Naseri M, Banihasan M, Alamdaran SA. Prediction of renal cortical involvement using serum and urinary inflammatory markers in children with febrile urinary tract infection. Iranian Journal of Radiology 2017;14(2):e41485. [EMBASE: 617759856]
Neuhaus 2008 {published data only}
-
- Neuhaus TJ, Berger C, Buechner K, Parvex P, Bischoff G, Goetschel P, et al. Randomised trial of oral versus sequential intravenous/oral cephalosporins in children with pyelonephritis. European Journal of Pediatrics 2008;167(9):1037-47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nickavar 2015 {published data only}
Oh 2010 {published data only}
-
- Oh MM, Cheon J, Kang SH, Park HS, Lee JG, Moon du G. Predictive factors for acute renal cortical scintigraphic lesion and ultimate scar formation in children with first febrile urinary tract infection. Journal of Urology 2010;183(3):1146-50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Oh 2011 {published data only}
-
- Oh M, Moon DG, Bae JH, Kang SH, Kim JJ, Lee JG, et al. The role of therapeutic delay time in acute scintigraphic lesion and ultimate scar formation in children with first febrile UTI; is there difference according to the presence of vesico-ureteral reflux? [abstract]. Journal of Urology 2011;185(4 Suppl 1):e230-1. [EMBASE: 70377836]
Ohta 2019 {published data only}
-
- Ohta N, Yasudo H, Mizutani M, Matsushige T, Fukano R, Kittaka S, et al. Serum soluble ST2 as a marker of renal scar in pediatric upper urinary tract infection. Cytokine 2019;120:258-63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Orlowska 2004 {published data only}
-
- Orlowska H, Roszkowska-Blaim M. Procalcitonin - a new inflammatory marker in children with urinary tract infection - a preliminary study [Prokalcytonina - Nowy marker stanu zapalnego u dzieci z zakazeniem ukladu moczowego - Doniesienie wstepne]. Pediatria Polska 2004;79(2):111-4. [EMBASE: 38404888]
Otto 2005 {published data only}
-
- Otto G, Burdick M, Strieter R, Godaly G. Chemokine response to febrile urinary tract infection. Kidney International 2005;68(1):62-70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Otukesh 2009 {published data only}
-
- Otukesh H, Fereshtehnejad SM, Hoseini R, Hekmat S, Chalian H, Chalian M, et al. Urine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in children with urinary tract infection: a possible predictor of acute pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 2009;24(1):105-11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Paripovic 2011 {published data only}
-
- Paripovic A, Stajic N, Putnik J, Slavkovic B, Jaksic E, Bogdanovic R. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in urine of children with acute pyelonephritis [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2011;26(9):1691-2. [EMBASE: 70530833]
Pecile 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pecile P, Miorin E, Romanello C, Falleti E, Valent F, Giacomuzzi F, et al. Procalcitonin: a marker of severity of acute pyelonephritis among children. Pediatrics 2004;144(2):e249-54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pecile 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pecile P, Miorin E, Romanello C, Falleti E, Valent F, Giacomuzzi F, et al. Procalcitonin: a marker of severity of acute pyelonephritis among children: commentary. Archives de Pediatrie 2005;12(7):1155-6. [EMBASE: 40835238] - PubMed
Pecile 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pecile P, Romanello C. Procalcitonin and pyelonephritis in children. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases 2007;20(1):83-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Piepsz 1998 {published data only}
-
- Piepsz A, Tamminen-Mobius T, Reiners C, Heikkila J, Kivisaari A, Nilsson NJ, et al. Five-year study of medical or surgical treatment in children with severe vesico-ureteral reflux dimercaptosuccinic acid findings. International Reflux Study Group in Europe. European Journal of Pediatrics 1998;157(9):753-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Prat 2003 {published data only}
-
- Prat C, Dominguez J, Rodrigo C, Gimenez M, Azuara M, Jimenez O, et al. Elevated serum procalcitonin values correlate with renal scarring in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2004;22(5):438-42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Prat 2004 {published data only}
-
- Prat C, Dominguez J, Rodrigo C, Gimenez M, Azuara M, Blanco S, et al. Use of quantitative and semiquantitative procalcitonin measurements to identify children with sepsis and meningitis. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2004;23(2):136-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Preda 2011 {published data only}
-
- Preda I, Jodal U, Sixt R, Stokland E, Hansson S. Imaging strategy for infants with urinary tract infection: a new algorithm. Journal of Urology 2011;185(3):1046-52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Printza 2008 {published data only}
-
- Printza N, Papachristou F, Piretzi K, Goga C, Arsos G. Neither clinical nor biological data can predict renal involvement in infants with febrile urinary tract infection [abstract]. Pediatrics 2008;121(Suppl 2):S143.
Puczko‐Michalczuk 2008 {published data only}
-
- Puczko-Michalczuk A, Zoch-Zwierz W, Wasilewska A, Porowska T, Korzeniecka-Kozerska A. Evaluation of inflammatory and renal injury markers in youngest children with pyelonephritis [Ocena wskaznikow zapalenia i uszkodzenia nerek u najmlodszych dzieci chorych na odmiedniczkowe zapalenie nerek]. Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski 2008;25(150):451-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Putnik 2011 {published data only}
-
- Putnik J, Stajic N, Paripovic A, Jaksic E, Bogdanovic R. Procalcitonin as a predictor of acute pyelonephritis and risk for renal scarring in children with a first febrile urinary tract infection [abstract]. Pediatric Nephrology 2011;26(9):1701-2. [EMBASE: 70530865]
Repetto 2004 {published data only}
-
- Repetto HA, Alarcon PA, Pellegrini M. Procalcitonin as a marker of acute pyelonephritis. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;18(7):726. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Robles 2005 {published data only}
-
- Robles Garcia B, Rodriguez Fernandez LM, Suarez Rodriguez MA, Marugan De Miguelsanz JM, Fernandez Castano M, Fuentes Acebes MC. Comparison of the utility of fever and some laboratory parameters to diagnose acute pyelonephritis in children [Comparacion de la utilidad de la fiebre y de algunos parametros analiticos para el diagnostico de pielonefritis aguda en ninos]. Revista Espanola de Pediatria 2005;61(5):358-63. [EMBASE: 43010352]
Sadeghi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sadeghi BS, Hashemi M. Diagnostic evaluation of procalcitonin in children with acute pyelonephritis [abstract]. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2011;5(Suppl 1):15. [EMBASE: 70539635]
Sellem 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sellem A, Elajmi W, Mahjoub Y, Hammami H. Interest of DMSA renal scintigraphy in acute pyelonephritis in children [Interet de la scintigraphie renale au DMSA dans les pyelonephrites aigues de l'enfant]. Medecine Nucleaire 2013;37(10-11):455-61. [EMBASE: 52833969]
Sevketoglu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sevketoglu E, Yilmaz A, Gedikbasi A, Karyagar S, Kiyak A, Mulazimoglu M, et al. Urinary macrophage migration inhibitory factor in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatric Nephrology 2010;25(2):299-304. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sheu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sheu JN, Chen SM, Meng MH, Lue KH. The role of serum and urine interleukin-8 on acute pyelonephritis and subsequent renal scarring in children. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2009;28(10):885-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sim 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sim JH, Yim HE, Choi BM, Lee JH, Yoo KH. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts acute pyelonephritis in children with urinary tract infections. Pediatric Research 2015;78(1):48-55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simren 2018 {published data only}
-
- Simrén Y, Valdimarsson S, Stokland E, Lagerstrand KM, Sixt R, Hansson S. Renal swelling indicates renal damage in infants with their first urinary tract infection. Acta Paediatrica 2018;107(11):2004-10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simsek 2004 {published data only}
-
- Simsek E, Kologlu N, Yugunt I, Kocabay K. Comparison of imaging studies and diagnostic tests for the diagnosis and follow-up of recurrent urinary tract infection in children. International Pediatrics 2004;19(2):109-13. [EMBASE: 38747472]
Smolkin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Smolkin V, Koren A, Raz R, Colodner R, Sakran W, Halevy R. Procalcitonin as a marker of acute pyelonephritis in infants and children. Pediatric Nephrology 2002;17(6):409-12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Soylu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Soylu A, Kasap B, Demir K, Turkmen M, Kavukcu S. Predictive value of clinical and laboratory variables for vesicoureteral reflux in children. Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22(6):844-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stokland 1996a {published data only}
-
- Stokland E, Hellstrom M, Jacobsson B, Jodal U, Lundgren P, Sixt R. Early 99mTc dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scintigraphy in symptomatic first-time urinary tract infection. Acta Paediatrica 1996;85(4):430-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stokland 1998 {published data only}
-
- Stokland E, Hellstrom M, Jacobsson B, Jodal U, Sixt R. Evaluation of DMSA scintigraphy and urography in assessing both acute and permanent renal damage in children. Acta Radiologica 1998;39(4):447-52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Subat‐Dezulovic 1998 {published data only}
-
- Subat-Dezulovic M, Katalinic-Franulovic J, Cekada S. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of the first documented urinary infection in children [Epidemioloske i klinicke osobitosti prve dokazane urinarne infekcije u djece]. Paediatria Croatica 1998;42(3-4):165-72. [EMBASE: 29067766]
Sun 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sun HL, Wu KH, Chen SM, Chao YH, Ku MS, Hung TW, et al. Role of procalcitonin in predicting dilating vesicoureteral reflux in young children hospitalized with a first febrile urinary tract infection. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2013;32(9):e348-54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Swerkersson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Swerkersson S, Jodal U, Sixt R, Stokland E, Hansson S. Relationship among vesicoureteral reflux, urinary tract infection and renal damage in children. Journal of Urology 2007;178(2):647-1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tealab 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tealab AA, Kholy O, Saad M, Gaballah A. The role of urinary IL 8 level in diagnosis and differentiation between different types of urinary tract infection in children [abstract]. European Urology, Supplements 2011;10(2):111. [EMBASE: 70375789]
Thayyil 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thayyil S, Shenoy M, Hamaluba M, Gupta A, Frater J, Verber IG. Is procalcitonin useful in early diagnosis of serious bacterial infections in children? Acta Paediatrica 2005;94(2):155-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Valavi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Valavi E, Ahmadzadeh A, Ziaee KT, Nicfar R, Aminzadeh M, Najafi R. Clinical correlation between findings of renal scintigraphy and clinical / laboratory findings in children with febrile UTI [abstract]. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2011;5(Suppl 1):10. [EMBASE: 70539623]
Verboven 1990 {published data only}
-
- Verboven M, Ingels M, Delree M, Piepsz A. 99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy in acute urinary tract infection in children. Pediatric Radiology 1990;20(7):540-2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vujevic 2017 {published data only}
-
- Vujevic M, Benzon B, Markic J. New prediction model for diagnosis of bacterial infection in febrile infants younger than 90 days. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017;59(3):261-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wang YT, Chiu NT, Chen MJ, Huang JJ, Chou HH, Chiou YY. Correlation of renal ultrasonographic findings with inflammatory volume from dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scans in children with acute pyelonephritis. Journal of Urology 2005;173(1):190-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Yen CW, Chen DH. Urinary tract infection in children. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology & Infection 1999;32(3):199-205. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Yu Q, Guo KP, Yi SW, Li S, Mo LY. Role of procalcitonin in the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children. Zhongguo Dangdai Erke Zazhi [Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics] 2013;15(2):85-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Bossuyt 2006
Coulthard 2009
-
- Coulthard MG, Lambert HJ, Keir MJ. Do systemic symptoms predict the risk of kidney scarring after urinary tract infection? Archives of Disease in Childhood 2009;94(4):278-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Craig 2000
-
- Craig JC, Wheeler DM, Irwig L, Howman-Giles RB. How accurate is dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis? A meta-analysis of experimental studies. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2000;41(6):986-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Freedman 2005
-
- Freedman AL, Urologic Diseases in America Project. Urologic diseases in North America Project: trends in resource utilization for urinary tract infections in children. Journal of Urology 2005;173(3):949-54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hanson 1983
-
- Hanson LA, Jodal U, Sabel KG, Wadsworth C. The diagnostic value of C-reactive protein. Pediatric Infectious Disease 1983;2(2):87-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hayen 2010
-
- Hayen A, Macaskill P, Irwig L, Bossuyt P. Appropriate statistical methods are required to assess diagnostic tests for replacement, add-on, and triage. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2010;63(8):883-91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hoberman 1994
-
- Hoberman A, Wald ER, Reynolds EA, Penchansky L, Charron M. Pyuria and bacteriuria in urine specimens obtained by catheter from young children with fever. Journal of Pediatrics 1994;124(4):513-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Huang 2011
-
- Huang YY, Chen MJ, Chiu NT, Chou HH, Lin KY, Chiou YY. Adjunctive oral methylprednisolone in pediatric acute pyelonephritis alleviates renal scarring. Pediatrics 2011;128(3):e496-504. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Leroy 2013
-
- Leroy S, Fernadez-Lopez A, Nikfar R, Romanello C, Bouissou F, Gervaix A, et al. Association of procalcitonin with acute pyelonephritis and renal scars in pediatric UTI. Pediatrics 2013;131(5):870-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mantadakis 2009
-
- Mantadakis E, Plessa E, Vouloumanou EK, Karageorgopoulos DE, Chatzimichael A, Falagas ME. Serum procalcitonin for prediction of renal parenchymal involvement in children with urinary tract infections: a meta-analysis of prospective clinical studies. Journal of Pediatrics 2009;155(6):875-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pylkkanen 1981
-
- Pylkkanen J Vilska J, Koskimies O. The value of level diagnosis of childhood urinary tract infection in predicting renal injury. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1981;70(6):879-83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
SAS 2011
-
- SAS Software [computer program]. SAS Institute Inc., North Carolina USA, 2011.
Shaikh 2007
-
- Shaikh N, Morone NE, Lopez J, Chianese J, Sangvai S, D'Amico F, et al. Does this child have a urinary tract infection? JAMA 2007;298(24):2895-904. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shaikh 2008
-
- Shaikh N, Morone NE, Bost JE, Farrell MH. Prevalence of urinary tract infection in childhood: a meta-analysis. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2008;27(4):302-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stokland 1996
-
- Stokland E, Hellstrom M, Jacobsson B, Jodal U, Sixt R. Renal damage one year after first urinary tract infection: role of dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy. Journal of Pediatrics 1996;129(6):815-20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529-36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Shaikh 2011
Shaikh 2015
-
- Shaikh N, Borrell JL, Evron J, Leeflang MM. Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 1. Art. No: CD009185. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009185.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

