Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract on Diabetes-Induced Alterations in Paraoxonase 1 and Catalase in Rats Analyzed through Progress Kinetic and Blind Docking
- PMID: 32911700
- PMCID: PMC7555439
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9090840
Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract on Diabetes-Induced Alterations in Paraoxonase 1 and Catalase in Rats Analyzed through Progress Kinetic and Blind Docking
Abstract
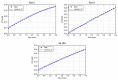
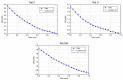
In our study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of Moringa oleifera leaves extract on rat paraoxonase 1 (rPON1) and catalase (rCAT) activities in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Our study included three groups; group C (control, n = 5); group D (diabetic, n = 5); and group DM (M. oleifera extract-supplemented diabetic rats, n = 5). Daily oral administration of M. oleifera extract at 200 mg/kg doses produced an increase in endogenous antioxidants. Serum rPON1 (lactonase) and liver cytosol catalase activities were determined by a spectrophotometric assay using progress curve analysis. We found a decrease in the Vm value of rPON1 in diabetic rats, but dihydrocoumarin (DHC) affinity (Km) was slightly increased. The value of Vm for the DM group was found to be reduced approximately by a factor of 3 compared with those obtained for group C, whereas Km was largely changed (96 times). Catalase activity was significantly higher in the DM group. These data suggest that the activation of rPON1 and rCAT activities by M. oleifera extracts may be mediated via the effect of the specific flavonoids on the enzyme structure. In addition, through molecular blind docking analysis, rPON1 was found to have two binding sites for flavonoids. In contrast, flavonoids bound at four sites in rCAT. In conclusion, the data suggest that compounds from M. oleifera leaves extract were able to influence the catalytic activities of both enzymes to compensate for the changes provoked by diabetes in rats.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera leaves extract; progress kinetics and blind docking; rat liver catalase; serum paraoxonase 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Anti-Hyperglycaemic, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of the Methanol Extract of Moringa Oleifera in Diabetes-Induced Nephrotoxic Male Wistar Rats.Molecules. 2017 Mar 23;22(4):439. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040439. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28333074 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on cardiac antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 4;5(12):e02935. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02935. eCollection 2019 Dec. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31872118 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic administration of ethanol leaf extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. (Moringaceae) may compromise glycaemic efficacy of Sitagliptin with no significant effect in retinopathy in a diabetic rat model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 24;194:895-903. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.065. Epub 2016 Oct 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27789327
-
Moringa oleifera leaf extract ameliorates alloxan-induced diabetes in rats by regeneration of β cells and reduction of pyruvate carboxylase expression.Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;92(5):413-9. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2014-0081. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25289966
-
Effects of Moringa oleifera aqueous leaf extract in alloxan induced diabetic mice.Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016 Sep;8(3):109-117. doi: 10.1556/1646.8.2016.3.7. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016. PMID: 28203392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review on the Antidiabetic Properties of Moringa oleifera Extracts: Focusing on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation as Main Therapeutic Targets.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 11;13:940572. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.940572. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35899107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals as Modulators of Paraoxonase-1 in Health and Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;11(7):1273. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071273. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Removal of Time-Concentration Data Points from Progress Curves Improves the Determination of Km: The Example of Paraoxonase 1.Molecules. 2022 Feb 15;27(4):1306. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041306. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209091 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Polyphenols in Modulating PON1 Activity Regarding Endothelial Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 4;25(5):2962. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052962. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcitriol Induces Paraoxonase 1 Expression in HepG2 Cells: Possible Involvement of VDR-Dependent and Alternative Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 18;26(16):7948. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167948. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cournot M., Burillo E., Saulnier P., Planesse C., Gand E., Rehman M., Ragot S., Rondeau P., Catan A., Gonthier M., et al. Circulating Concentrations of Redox Biomarkers Do Not Improve the Prediction of Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018;7:e007397. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007397. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

