Polyphenols vs. Coronaviruses: How Far Has Research Moved Forward?
- PMID: 32911757
- PMCID: PMC7570460
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184103
Polyphenols vs. Coronaviruses: How Far Has Research Moved Forward?
Abstract
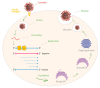
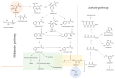
The epidemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2 at the beginning of 2020, led us to a serious change in our lifestyle that for about three months has confined us to our homes, far from our laboratory routine. In this period, the belief that the work of a researcher should never stop has been the driving force in writing the present paper. It aims at reviewing the recent scientific knowledge about in vitro experimental data that focused on the antiviral role of phenols and polyphenols against different species of coronaviruses (CoVs), pointing up the viral targets potentially involved. In the current literature scenario, the papain-like and the 3-chymotrypsin-like proteases seem to be the most deeply investigated and a number of isolated natural (poly)phenols has been screened for their efficacy.
Keywords: 3-chymotrypsin-like protease; antiviral activity; coronavirus; herbal extracts; papain-like protease; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Structural-based virtual screening and in vitro assays for small molecules inhibiting the feline coronavirus 3CL protease as a surrogate platform for coronaviruses.Antiviral Res. 2020 Oct;182:104927. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104927. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32910955 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization Rules for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Antivirals: Ensemble Docking and Exploration of the Coronavirus Protease Active Site.Viruses. 2020 Aug 26;12(9):942. doi: 10.3390/v12090942. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32859008 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Fluorescence-Based, High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Reporter Assay.J Virol. 2020 Oct 27;94(22):e01265-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01265-20. Print 2020 Oct 27. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32843534 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2.Malays J Pathol. 2020 Apr;42(1):3-11. Malays J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32342926 Review.
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Nanoscale Materials Against Coronaviruses-Possible Potential Antiviral Agents for SARS-CoV-2.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2020 Jul;19(3):485-497. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2020.2997257. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2020. PMID: 32603297
Cited by
-
Promising Antiviral Activities of Natural Flavonoids against SARS-CoV-2 Targets: Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 14;22(20):11069. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011069. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681727 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic compounds versus SARS-CoV-2: An update on the main findings against COVID-19.Heliyon. 2022 Sep 20;8(9):e10702. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10702. eCollection 2022 Sep. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36157310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Biomaterial on Sutures, Bandages and Face Masks with Potential for Infection Control.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 10;14(10):1932. doi: 10.3390/polym14101932. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631817 Free PMC article.
-
Probing marine brown macroalgal phlorotannins as antiviral candidate against SARS-CoV-2: molecular docking and dynamics simulation approach.Mol Divers. 2022 Dec;26(6):3205-3224. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10383-y. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Mol Divers. 2022. PMID: 35152367 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Properties of Lepidium sativum L. Facilitated Silver Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 27;13(9):1352. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091352. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575428 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

