Resistance Exercise, Electrical Muscle Stimulation, and Whole-Body Vibration in Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 32911822
- PMCID: PMC7563530
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9092902
Resistance Exercise, Electrical Muscle Stimulation, and Whole-Body Vibration in Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
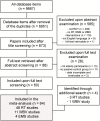
It has been shown that resistance exercise (RT) is one of the most effective approaches to counteract the physical and functional changes associated with aging. This systematic review with meta-analysis compared the effects of RT, whole-body vibration (WBV), and electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) on muscle strength, body composition, and functional performance in older adults. A thorough literature review was conducted, and the analyses were limited to randomized controlled trials. In total, 63 studies were included in the meta-analysis (48 RT, 11 WBV, and 4 EMS). The results showed that RT and WBV are comparably effective for improving muscle strength, while the effects of EMS remains debated. RT interventions also improved some outcome measures related to functional performance, as well as the cross-sectional area of the quadriceps. Muscle mass was not significantly affected by RT. A limitation of the review is the smaller number of WBV and particularly EMS studies. For this reason, the effects of WBV and EMS could not be comprehensively compared to the effect of RT for all outcome measures. For the moment, RT or combinations of RT and WBV or EMS, is probably the most reliable way to improve muscle strength and functional performance, while the best approach to increase muscle mass in older adults remains open to further studies.
Keywords: elderly; electrical stimulation; falls; resistance exercise; sarcopenia; vibration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

