A Case of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Salvage Therapy for COVID-19-Associated Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Mounting Evidence
- PMID: 32911986
- PMCID: PMC7488892
- DOI: 10.1177/2324709620957778
A Case of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Salvage Therapy for COVID-19-Associated Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Mounting Evidence
Abstract
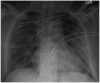
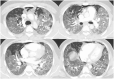
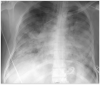
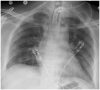
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by a novel human coronavirus has led to a tsunami of viral illness across the globe, originating from Wuhan, China. Although the value and effectiveness of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in severe respiratory illness from COVID-19 remains unclear at this time, there is emerging evidence suggesting that it could be utilized as an ultimate treatment in appropriately selected patients not responding to conventional care. We present a case of a 32-year-old COVID-19 positive male with a history of diabetes mellitus who was intubated for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The patient's hypoxemia failed to improve despite positive pressure ventilation, prone positioning, and use of neuromuscular blockade for ventilator asynchrony. He was evaluated by a multidisciplinary team for considering ECMO for refractory ARDS. He was initiated on venovenous ECMO via dual-site cannulation performed at the bedside. Although his ECMO course was complicated by bleeding, he showed a remarkable improvement in his lung function. ECMO was successfully decannulated after 17 days of initiation. The patient was discharged home after 47 days of hospitalization without any supplemental oxygen and was able to undergo active physical rehabilitation. A multidisciplinary approach is imperative in the initiation and management of ECMO in COVID-19 patients with severe ARDS. While ECMO is labor-intensive, using it in the right phenotype and in specialized centers may lead to positive results. Patients who are young, with fewer comorbidities and single organ dysfunction portray a better prognosis for patients in which ECMO is utilized.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; ECMO; acute respiratory distress syndrome; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Clinical Course of COVID-19 Pneumonia and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in 2 Passengers from the Cruise Ship Diamond Princess in February 2020.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Aug 19;21:e926835. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.926835. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32811804 Free PMC article.
-
[ECMO Therapy in a Case of Severe ARDS Related to COVID-19].Pneumologie. 2020 Jul;74(7):423-428. doi: 10.1055/a-1199-2167. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Pneumologie. 2020. PMID: 32674191 German.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study.Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Nov;8(11):1121-1131. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30328-3. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32798468 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Respiratory Failure During Respiratory Epidemics and Pandemics: A Narrative Review.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2020 Apr;49(4):199-214. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2020. PMID: 32296808 Review.
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) in Critically Ill Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).Med Sci Monit. 2020 Aug 6;26:e925364. doi: 10.12659/MSM.925364. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32759887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and rehabilitation in patients with COVID-19: A scoping review.Artif Organs. 2022 Jan;46(1):30-39. doi: 10.1111/aor.14110. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Artif Organs. 2022. PMID: 34778984 Free PMC article.
-
A successful case of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: walking home without oxygen supplementation.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2021 Jun 21;11(4):480-484. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2021.1918442. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2021. PMID: 34211653 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes in patients co-infected with COVID-19 and Staphylococcus aureus: a scoping review.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 21;21(1):985. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06616-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34548027 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary ARDS Following Acute Pancreatitis: Is Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Feasible or Futile?J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 2;10(5):1000. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051000. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33801239 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

