Adduction-Induced Strain on the Optic Nerve in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma at Normal Intraocular Pressure
- PMID: 32911989
- PMCID: PMC7947028
- DOI: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1817491
Adduction-Induced Strain on the Optic Nerve in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma at Normal Intraocular Pressure
Abstract
Purpose/aim: The optic nerve (ON) becomes taut during adduction beyond ~26° in healthy people and patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG), but only retracts the globe in POAG. We used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to investigate this difference.
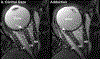
Materials and methods: MRI was obtained in 2-mm quasi-coronal planes in central gaze, and smaller (~23-25°) and larger (~30-31°) adduction and abduction in 21 controls and 12 POAG subjects whose intraocular pressure never exceeded 21 mmHg. ON cross-sections were analyzed from the globe to 10 mm posteriorly. Area centroids were used to calculate ON path lengths and changes in cross-sections to calculate elongation assuming volume conservation.
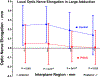
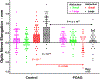
Results: For both groups, ON path was nearly straight (<102.5% of minimum path) in smaller adduction, with minimal further straightening in larger adduction. ON length was redundant in abduction, exceeding 103% of minimum path for both groups. For normals, the ON elongated 0.4 ± 0.5 mm from central gaze to smaller adduction, and 0.4 ± 0.5 mm further from smaller to larger adduction. For POAG subjects, the ON did not elongate on average from central gaze to smaller adduction and only 0.2 ± 0.4 mm from smaller to larger adduction (P = .045 vs normals). Both groups demonstrated minimal ON elongation not exceeding 0.25 mm from central gaze to smaller and larger abduction. The globe retracted significantly more during large adduction in POAG subjects than normals (0.6 ± 0.7 mm vs 0.2 ± 0.5 mm, P = .027), without appreciable retraction in abduction. For each mm increase in globe axial length, ON elongation in large adduction similarly increased by 0.2 mm in each group.
Conclusions: The normal ON stretches to absorb force and avert globe retraction in adduction. In POAG with mild to severe visual field loss, the relatively inelastic ON tethers and retracts the globe during adduction beyond ~26°, transfering stress to the optic disc that could contribute to progressive neuropathy during repeated eye movements.
Keywords: Biomechanics; normal tension glaucoma; optic nerve; optic nerve strain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Optic Nerve Traction During Adduction in Open Angle Glaucoma with Normal versus Elevated Intraocular Pressure.Curr Eye Res. 2020 Feb;45(2):199-210. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1660371. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31453714 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Optic Nerve Traction During Adduction in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma With Normal Intraocular Pressure.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Aug 1;58(10):4114-4125. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22093. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28829843 Free PMC article.
-
Eye Movements and the Intraorbital Subarachnoid Space: Potential Contribution of Altered Cerebrospinal Fluid Pumping in Optic Neuropathies.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jan 2;66(1):53. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.1.53. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39847366 Free PMC article.
-
Optic Nerve Sheath Tethering in Adduction Occurs in Esotropia and Hypertropia, But Not in Exotropia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Jun 1;59(7):2899-2904. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24305. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30025141 Free PMC article.
-
The potential impact of a vegetarian diet on glaucoma.Surv Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep-Oct;69(5):833-841. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2024.05.001. Epub 2024 May 18. Surv Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38768761 Review.
Cited by
-
Material properties and effect of preconditioning of human sclera, optic nerve, and optic nerve sheath.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021 Aug;20(4):1353-1363. doi: 10.1007/s10237-021-01448-2. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021. PMID: 33877503 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Optic Nerve Head Blood Flow During Horizontal Ocular Duction.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Jan 2;65(1):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.1.7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38170537 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Demonstrates Strain and Volume Effects on Optic Disk and Peripapillary Vasculature Caused by Horizontal Duction.Curr Eye Res. 2023 May;48(5):518-527. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2023.2172185. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Curr Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 36843550 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Peripapillary Intrachoroidal Cavitation and Myopic Peripapillary Distortions in Polar Regions by Optical Coherence Tomography.Clin Ophthalmol. 2022 Aug 13;16:2617-2629. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S376597. eCollection 2022. Clin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35992567 Free PMC article.
-
Postmortem Digital Image Correlation and Finite Element Modeling Demonstrate Posterior Scleral Deformations during Optic Nerve Adduction Tethering.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 May 2;11(5):452. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11050452. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790319 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
