Radiation-induced lung toxicity - cellular and molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis, management, and literature review
- PMID: 32912295
- PMCID: PMC7488099
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-020-01654-9
Radiation-induced lung toxicity - cellular and molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis, management, and literature review
Abstract
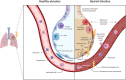
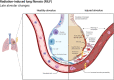
Lung, breast, and esophageal cancer represent three common malignancies with high incidence and mortality worldwide. The management of these tumors critically relies on radiotherapy as a major part of multi-modality care, and treatment-related toxicities, such as radiation-induced pneumonitis and/or lung fibrosis, are important dose limiting factors with direct impact on patient outcomes and quality of life. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of radiation-induced pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis, present predictive factors as well as recent diagnostic and therapeutic advances. Novel candidates for molecularly targeted approaches to prevent and/or treat radiation-induced pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that competing interests do not exist.
Figures
References
-
- Delaney G, Barton M, Jacob S, Jalaludin B. A model for decision making for the use of radiotherapy in lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:120–128. - PubMed
-
- Nestle U, Schimek-Jasch T, Kremp S, Schaefer-Schuler A, Mix M, Küsters A, Tosch M, Hehr T, Eschmann SM, Bultel YP, Hass P. Imagingbased target volume reduction in chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (PET-Plan): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2020;21(4):581–92. - PubMed
-
- Chun S, Hu C, Choy H, Komaki R, Timmerman R, Schild S, Bogart J, Dobelbower M, Bosch W, Galvin J. Comparison of 3-D conformal and intensity modulated radiation therapy outcomes for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer in NRG oncology/RTOG 0617. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:S1–S2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

