Central diabetes insipidus caused by a pituitary stalk germinoma resembling infundibuloneurohypophysitis
- PMID: 32912882
- PMCID: PMC7482447
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-234724
Central diabetes insipidus caused by a pituitary stalk germinoma resembling infundibuloneurohypophysitis
Abstract
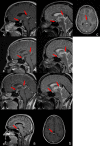
We report the case of a pituitary stalk germinoma initially misdiagnosed and treated as infundibuloneurohypophysitis (INH). A 27-year-old man presented with a 1-year history of polydipsia, polyuria, nycturia consistent with central diabetes insipidus and a hyperintense pituitary stalk lesion on MRI. A possible INH diagnosis was considered, after excluding other pathologies. Lesion biopsy was discarded at that time on the ground of a small target and the high risk of added morbidity. Oral desmopressin led to initial symptoms resolution but, in the following months, an anterior panhypopituitarism developed, in spite of appropriate treatment and, by that time, the brain MRI also revealed lesion growth, which prompted a biopsy recommendation. The pathology analysis revealed a germinoma. After chemotherapy and radiotherapy, there was complete disappearance of the pituitary lesion, but the panhypopituitarism persisted. In conclusion, this case highlights the importance and difficulty of precise diagnosis in the initial assessment of pituitary stalk lesions and the need for close monitoring of treatment response. Diagnostic reassessment and biopsy in atypical cases is the only path to achieve the correct diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: CNS cancer; pituitary disorders.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Prete A, Salvatori R. Hypophysitis. 2018. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc, 2000. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519842/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
