Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Three Novel Susceptibility Loci and Reveals Ethnic Heterogeneity of Genetic Susceptibility for IgA Nephropathy
- PMID: 32912934
- PMCID: PMC7790208
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019080799
Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Three Novel Susceptibility Loci and Reveals Ethnic Heterogeneity of Genetic Susceptibility for IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Eighteen known susceptibility loci for IgAN account for only a small proportion of IgAN risk.
Methods: Genome-wide meta-analysis was performed in 2628 patients and 11,563 controls of Chinese ancestry, and a replication analysis was conducted in 6879 patients and 9019 controls of Chinese descent and 1039 patients and 1289 controls of European ancestry. The data were used to assess the association of susceptibility loci with clinical phenotypes for IgAN, and to investigate genetic heterogeneity of IgAN susceptibility between the two populations. Imputation-based analysis of the MHC/HLA region extended the scrutiny.
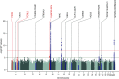
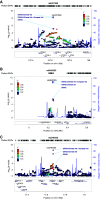
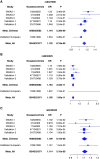
Results: Identification of three novel loci (rs6427389 on 1q23.1 [P=8.18×10-9, OR=1.132], rs6942325 on 6p25.3 [P=1.62×10-11, OR=1.165], and rs2240335 on 1p36.13 [P=5.10×10-9, OR=1.114]), implicates FCRL3, DUSP22.IRF4, and PADI4 as susceptibility genes for IgAN. Rs2240335 is associated with the expression level of PADI4, and rs6427389 is in high linkage disequilibrium with rs11264799, which showed a strong expression quantitative trail loci effect on FCRL3. Of the 24 confirmed risk SNPs, six showed significant heterogeneity of genetic effects and DEFA showed clear evidence of allelic heterogeneity between the populations. Imputation-based analysis of the MHC region revealed significant associations at three HLA polymorphisms (HLA allele DPB1*02, AA_DRB1_140_32657458_T, and AA_DQA1_34_32717152) and two SNPs (rs9275464 and rs2295119).
Conclusions: A meta-analysis of GWAS data revealed three novel genetic risk loci for IgAN, and three HLA polymorphisms and two SNPs within the MHC region, and demonstrated the genetic heterogeneity of seven loci out of 24 confirmed risk SNPs. These variants may explain susceptibility differences between Chinese and European populations.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; common variants; genome-wide association study; meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Berger J, Hinglais N: [Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG]. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 74: 694–695, 1968. - PubMed
-
- Wyatt RJ, Julian BA: IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med 368: 2402–2414, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Zhou FD, Zhao MH, Zou WZ, Liu G, Wang H: The changing spectrum of primary glomerular diseases within 15 years: A survey of 3331 patients in a single Chinese centre. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24: 870–876, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Li LS, Liu ZH: Epidemiologic data of renal diseases from a single unit in China: Analysis based on 13,519 renal biopsies. Kidney Int 66: 920–923, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Pan X, Xu J, Ren H, Zhang W, Xu Y, Shen P, et al. : Changing spectrum of biopsy-proven primary glomerular diseases over the past 15 years: A single-center study in China. Contrib Nephrol 181: 22–30, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

