Association of serum uric acid, morning home blood pressure and cardiovascular risk factors in a population with previous prehypertension: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 32912954
- PMCID: PMC7482459
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038046
Association of serum uric acid, morning home blood pressure and cardiovascular risk factors in a population with previous prehypertension: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: To observe the changes in blood pressure (BP) over 10 years and to investigate current BP association to serum uric acid (SUA) levels and cardiovascular risk factors in the epidemiological data of a target group of patients with prehypertension in 2007.
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Setting: Mlati Subdistrict, Sleman District, Yogyakarta Province, Indonesia.
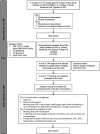
Participants: A total of 733 patients from 'Mlati Study Database' in 2007 were selected by simple random sampling using statistical software. Subjects had both physical and laboratory examinations.
Outcome measures: Morning home BP and laboratory examination of urine (uric acid excretion and creatinine) and blood samples (SUA, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, a lipid profile and fasting blood glucose levels).
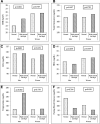
Results: About 31.1% of 733 subjects with prehypertension became hypertensive after 10 years, 24.6% returned to normal tension and the rest of it remained in prehypertensive state. Mean (SD) of SUA levels in 2017 was significantly higher in men than in women (5.78 (1.25) mg/dL vs 4.52 (1.10) mg/dL, p<0.001). Furthermore, men tended to have high-normal (5-7 mg/dL) or high SUA levels (≥7 mg/dL) compared with women (p<0.001, Relative Risk (RR)=2.60). High-normal and high SUA levels in population with a history of prehypertension were significantly associated with current prehypertension and hypertension only in women (p=0.001, RR=1.21). Age and body mass index was found to be significantly associated with both systolic and diastolic BP in men, but only with systolic BP in women. Fasting blood glucose and SUA levels were significantly associated with systolic and diastolic BP only in women.
Conclusion: We concluded that after 10 years, of 733 subjects with prehypertension, 31.1% became hypertensive. The SUA levels in men are significantly higher than those in women. Moreover, high-normal and high SUA levels were significantly associated with prehypertension and hypertension in women but not in men.
Keywords: epidemiology; hypertension; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Annual Health Research Report Division of research and health development: Indonesian Ministry of health 2013.
-
- Ruchira P, Gajendra Singh M. Ps 15-11 impact of hypertension on quality of life among people living in an urban area of Delhi, India. J Hypertens 2016;34:e462.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
