The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 in Europe and North America
- PMID: 32912998
- PMCID: PMC7810038
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abc8169
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 in Europe and North America
Abstract
Accurate understanding of the global spread of emerging viruses is critical for public health responses and for anticipating and preventing future outbreaks. Here we elucidate when, where, and how the earliest sustained severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission networks became established in Europe and North America. Our results suggest that rapid early interventions successfully prevented early introductions of the virus from taking hold in Germany and the United States. Other, later introductions of the virus from China to both Italy and Washington state, United States, founded the earliest sustained European and North America transmission networks. Our analyses demonstrate the effectiveness of public health measures in preventing onward transmission and show that intensive testing and contact tracing could have prevented SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks from becoming established in these regions.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

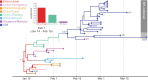

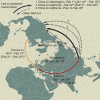
Update of
-
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 in Europe and the US.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 May 23:2020.05.21.109322. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.21.109322. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Science. 2020 Oct 30;370(6516):564-570. doi: 10.1126/science.abc8169. PMID: 32511416 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Trevor Bedford (@trvrb), “The team at the @seattleflustudy have sequenced the genome the #COVID19 community case reported yesterday from Snohomish County, WA, and have posted the sequence publicly to gisaid.org. There are some enormous implications here. 1/9” Twitter, 29 February 2020, 11:20 p.m.; https://twitter.com/trvrb/status/1233970271318503426.
-
- Bedford T., Greninger A. L., Roychoudhury P., Starita L. M., Famulare M., Huang M.-L., Nalla A., Pepper G., Reinhardt A., Xie H., Shrestha L., Nguyen T. N., Adler A., Brandstetter E., Cho S., Giroux D., Han P. D., Fay K., Frazar C. D., Ilcisin M., Lacombe K., Lee J., Kiavand A., Richardson M., Sibley T. R., Truong M., Wolf C. R., Nickerson D. A., Rieder M. J., Englund J. A., The Seattle Flu Study Investigators, Hadfield J., Hodcroft E. B., Huddleston J., Moncla L. H., Müller N. F., Neher R. A., Deng X., Gu W., Federman S., Chiu C., Duchin J. S., Gautom R., Melly G., Hiatt B., Dykema P., Lindquist S., Queen K., Tao Y., Uehara A., Tong S., MacCannell D., Armstrong G. L., Baird G. S., Chu H. Y., Shendure J., Jerome K. R., Cryptic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Washington state. Science 370, 571–575 (2020). 10.1126/science.abc0523 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fauver J. R., Petrone M. E., Hodcroft E. B., Shioda K., Ehrlich H. Y., Watts A. G., Vogels C. B. F., Brito A. F., Alpert T., Muyombwe A., Razeq J., Downing R., Cheemarla N. R., Wyllie A. L., Kalinich C. C., Ott I. M., Quick J., Loman N. J., Neugebauer K. M., Greninger A. L., Jerome K. R., Roychoudhury P., Xie H., Shrestha L., Huang M.-L., Pitzer V. E., Iwasaki A., Omer S. B., Khan K., Bogoch I. I., Martinello R. A., Foxman E. F., Landry M. L., Neher R. A., Ko A. I., Grubaugh N. D., Coast-to-Coast Spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the Early Epidemic in the United States. Cell 181, 990–996.e5 (2020). 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Reiche A. S., Hernandez M. M., Sullivan M. J., Ciferri B., Alshammary H., Obla A., Fabre S., Kleiner G., Polanco J., Khan Z., Alburquerque B., van de Guchte A., Dutta J., Francoeur N., Melo B. S., Oussenko I., Deikus G., Soto J., Sridhar S. H., Wang Y.-C., Twyman K., Kasarskis A., Altman D. R., Smith M., Sebra R., Aberg J., Krammer F., García-Sastre A., Luksza M., Patel G., Paniz-Mondolfi A., Gitman M., Sordillo E. M., Simon V., van Bakel H., Introductions and early spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the New York City area. Science 369, 297–301 (2020). 10.1126/science.abc1917 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deng X., Gu W., Federman S., du Plessis L., Pybus O. G., Faria N. R., Wang C., Yu G., Bushnell B., Pan C.-Y., Guevara H., Sotomayor-Gonzalez A., Zorn K., Gopez A., Servellita V., Hsu E., Miller S., Bedford T., Greninger A. L., Roychoudhury P., Starita L. M., Famulare M., Chu H. Y., Shendure J., Jerome K. R., Anderson C., Gangavarapu K., Zeller M., Spencer E., Andersen K. G., MacCannell D., Paden C. R., Li Y., Zhang J., Tong S., Armstrong G., Morrow S., Willis M., Matyas B. T., Mase S., Kasirye O., Park M., Masinde G., Chan C., Yu A. T., Chai S. J., Villarino E., Bonin B., Wadford D. A., Chiu C. Y., Genomic surveillance reveals multiple introductions of SARS-CoV-2 into Northern California. Science 369, 582–587 (2020). 10.1126/science.abb9263 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

