The impact of sex on gene expression across human tissues
- PMID: 32913072
- PMCID: PMC8136152
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aba3066
The impact of sex on gene expression across human tissues
Abstract
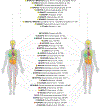
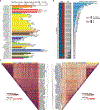
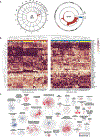
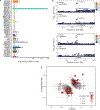
Many complex human phenotypes exhibit sex-differentiated characteristics. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying these differences remain largely unknown. We generated a catalog of sex differences in gene expression and in the genetic regulation of gene expression across 44 human tissue sources surveyed by the Genotype-Tissue Expression project (GTEx, v8 release). We demonstrate that sex influences gene expression levels and cellular composition of tissue samples across the human body. A total of 37% of all genes exhibit sex-biased expression in at least one tissue. We identify cis expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) with sex-differentiated effects and characterize their cellular origin. By integrating sex-biased eQTLs with genome-wide association study data, we identify 58 gene-trait associations that are driven by genetic regulation of gene expression in a single sex. These findings provide an extensive characterization of sex differences in the human transcriptome and its genetic regulation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

Comment in
-
Searching for sex differences.Science. 2020 Sep 11;369(6509):1298-1299. doi: 10.1126/science.abd8340. Science. 2020. PMID: 32913086 No abstract available.
-
Reaching completion for GTEx.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 Dec;21(12):717. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-00296-7. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 33060849 No abstract available.
-
Ubiquitous sex differences in tissue gene expression: the dawn of a new era for gender medicine.Eur Heart J. 2020 Nov 7;41(42):4090-4091. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa877. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 33245328 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH107666/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109905/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH106842/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007598/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG009916/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142028/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006855/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA229618/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011138/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH104393/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010480/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008150/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008901/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007593/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM124486/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090936/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK110919/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002585/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002550/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HG009987/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090941/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM122924/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG009494/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HG010718/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG003284/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM108711/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

