Understanding diaschisis models of attention dysfunction with rTMS
- PMID: 32913263
- PMCID: PMC7483730
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71692-6
Understanding diaschisis models of attention dysfunction with rTMS
Abstract
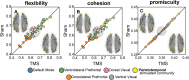
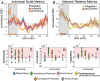
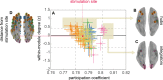
Visual attentive tracking requires a balance of excitation and inhibition across large-scale frontoparietal cortical networks. Using methods borrowed from network science, we characterize the induced changes in network dynamics following low frequency (1 Hz) repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) as an inhibitory noninvasive brain stimulation protocol delivered over the intraparietal sulcus. When participants engaged in visual tracking, we observed a highly stable network configuration of six distinct communities, each with characteristic properties in node dynamics. Stimulation to parietal cortex had no significant impact on the dynamics of the parietal community, which already exhibited increased flexibility and promiscuity relative to the other communities. The impact of rTMS, however, was apparent distal from the stimulation site in lateral prefrontal cortex. rTMS temporarily induced stronger allegiance within and between nodal motifs (increased recruitment and integration) in dorsolateral and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, which returned to baseline levels within 15 min. These findings illustrate the distributed nature by which inhibitory rTMS perturbs network communities and is preliminary evidence for downstream cortical interactions when using noninvasive brain stimulation for behavioral augmentations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

