Monitoring trends and differences in COVID-19 case-fatality rates using decomposition methods: Contributions of age structure and age-specific fatality
- PMID: 32913365
- PMCID: PMC7482960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238904
Monitoring trends and differences in COVID-19 case-fatality rates using decomposition methods: Contributions of age structure and age-specific fatality
Abstract
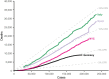
The population-level case-fatality rate (CFR) associated with COVID-19 varies substantially, both across countries at any given time and within countries over time. We analyze the contribution of two key determinants of the variation in the observed CFR: the age-structure of diagnosed infection cases and age-specific case-fatality rates. We use data on diagnosed COVID-19 cases and death counts attributable to COVID-19 by age for China, Germany, Italy, South Korea, Spain, the United States, and New York City. We calculate the CFR for each population at the latest data point and also for Italy, Germany, Spain, and New York City over time. We use demographic decomposition to break the difference between CFRs into unique contributions arising from the age-structure of confirmed cases and the age-specific case-fatality. In late June 2020, CFRs varied from 2.2% in South Korea to 14.0% in Italy. The age-structure of detected cases often explains more than two-thirds of cross-country variation in the CFR. In Italy, the CFR increased from 4.2% to 14.0% between March 9 and June 30, 2020, and more than 90% of the change was due to increasing age-specific case-fatality rates. The importance of the age-structure of confirmed cases likely reflects several factors, including different testing regimes and differences in transmission trajectories; while increasing age-specific case-fatality rates in Italy could indicate other factors, such as the worsening health outcomes of those infected with COVID-19. Our findings lend support to recommendations for data to be disaggregated by age, and potentially other variables, to facilitate a better understanding of population-level differences in CFRs. They also show the need for well-designed seroprevalence studies to ascertain the extent to which differences in testing regimes drive differences in the age-structure of detected cases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Bignami S, Ghio D. A demographic adjustment to improve measurement of COVID-19 severity at the developing stage of the pandemic. medRxiv preprint 2020; 2020.03.23.20040998. 10.1101/2020.03.23.20040998 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources