Genotypes and phenotypes of genes associated with achromatopsia: A reference for clinical genetic testing
- PMID: 32913385
- PMCID: PMC7479066
Genotypes and phenotypes of genes associated with achromatopsia: A reference for clinical genetic testing
Abstract
Purpose: Achromatopsia is a congenital autosomal recessive cone disorder, and it has been found to be associated with six genes. However, pathogenic variants in these six genes have been identified in patients with various retinal dystrophies with the exception of achromatopsia. Thus, this study aims to investigate the contribution of these genes in hereditary retinal diseases and the potential genotype-phenotype correlations.
Methods: Biallelic variants in six achromatopsia-related genes, namely, CNGA3, CNGB3, GNAT2, ATF6, PDE6C, and PDE6H, were analyzed based on data obtained from 7,195 probands with different eye conditions. A systematic genotype-phenotype analysis of these genes was performed based on these data, along with the data reported in the literature.
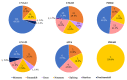
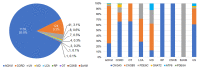
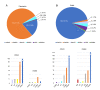
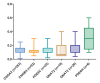
Results: Biallelic potential pathogenic variants (PPVs) in five of the six genes were identified in 119 probands with genetic eye diseases. The variants in CNGA3 were the most common and accounted for 81.5% (97/119). Of the 119 probands, 62.2% (74/119) have cone-rod dystrophy, whereas only 25.2% (30/119) have achromatopsia. No biallelic pathogenic variants in these genes were identified in patients with rod-dominant degeneration. A systematic review of genotypes and phenotypes revealed certain characteristics of each of the six genes, providing clues for the pathogenicity evaluation of the variants of the genes.
Conclusions: PPVs in the six genes were identified in various inherited retinal degeneration diseases, most of which are cone-dominant diseases but no rod-dominant diseases based on the data from a cohort of 7,195 probands with different eye conditions. The systematic genotype-phenotype analysis of these genes will be useful in drafting guidelines for the clinical genetic diagnostic application for the investigated genes.
Copyright © 2020 Molecular Vision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
THE GENETIC BASIS OF CLINICALLY SUSPECTED ACHROMATOPSIA IN THE UNITED ARAB EMIRATES.Retina. 2024 Nov 1;44(11):2019-2025. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000004218. Retina. 2024. PMID: 39024658
-
Cone cGMP-gated channel mutations and clinical findings in patients with achromatopsia, macular degeneration, and other hereditary cone diseases.Hum Mutat. 2005 Mar;25(3):248-58. doi: 10.1002/humu.20142. Hum Mutat. 2005. PMID: 15712225
-
Characterization of Retinal Structure in ATF6-Associated Achromatopsia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Jun 3;60(7):2631-2640. doi: 10.1167/iovs.19-27047. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31237654 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotyping and genotyping inherited retinal diseases: Molecular genetics, clinical and imaging features, and therapeutics of macular dystrophies, cone and cone-rod dystrophies, rod-cone dystrophies, Leber congenital amaurosis, and cone dysfunction syndromes.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024 May;100:101244. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2024.101244. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38278208 Review.
-
Comprehensive variant spectrum of the CNGA3 gene in patients affected by achromatopsia.Hum Mutat. 2022 Jul;43(7):832-858. doi: 10.1002/humu.24371. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 35332618 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Genetic Features of Korean Patients with Achromatopsia.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 18;14(2):519. doi: 10.3390/genes14020519. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833446 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of CNGA3-associated achromatopsia patient variants complements clinical genomics in pathogenicity determination.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 May 30;20(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03792-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40448196 Free PMC article.
-
Outer retinal transduction by AAV2-7m8 following intravitreal injection in a sheep model of CNGA3 achromatopsia.Gene Ther. 2022 Nov;29(10-11):624-635. doi: 10.1038/s41434-021-00306-1. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 34853444
-
Chromatic Pupillometry as a Putative Screening Tool for Heritable Retinal Disease in Rhesus Macaques.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Jun 1;12(6):13. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.6.13. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 38752621 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy for Achromatopsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 9;25(17):9739. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179739. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eksandh L, Kohl S, Wissinger B. Clinical features of achromatopsia in Swedish patients with defined genotypes. Ophthalmic Genet. 2002;23:109–20. - PubMed
-
- Fahim AT, Khan NW, Zahid S, Schachar IH, Branham K, Kohl S, Wissinger B, Elner VM, Heckenlively JR, Jayasundera T. Diagnostic fundus autofluorescence patterns in achromatopsia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156:1211–9. - PubMed
-
- Thiadens AA, Somervuo V, van den Born LI, Roosing S, van Schooneveld MJ, Kuijpers RW, van Moll-Ramirez N, Cremers FP, Hoyng CB, Klaver CC. Progressive loss of cones in achromatopsia: an imaging study using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:5952–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

