Ginsenoside Rh2 attenuates microglial activation against toxoplasmic encephalitis via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 32913400
- PMCID: PMC7471213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.06.002
Ginsenoside Rh2 attenuates microglial activation against toxoplasmic encephalitis via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Ginsenoside Rh2 (GRh2) is a characterized component in red ginseng widely used in Korea and China. GRh2 exhibits a wide range of pharmacological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. However, its effects on Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) infection have not been clarified yet.
Methods: The effect of GRh2 against T. gondii was assessed under in vitro and in vivo experiments. The BV2 cells were infected with tachyzoites of T. gondii RH strain, and the effects of GRh2 were evaluated by MTT assay, morphological observations, immunofluorescence staining, a trypan blue exclusion assay, reverse transcription PCR, and Western blot analyses. The in vivo experiment was conducted with BALB/c mice inoculated with lethal amounts of tachyzoites with or without GRh2 treatment.
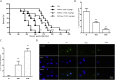
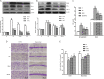
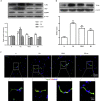
Results and conclusion: The GRh2 treatment significantly inhibited the proliferation of T. gondii under in vitro and in vivo studies. Furthermore, GRh2 blocked the activation of microglia and specifically decreased the release of inflammatory mediators in response to T. gondii infection through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. In mice, GRh2 conferred modest protection from a lethal dose of T. gondii. After the treatment, the proliferation of tachyzoites in the peritoneal cavity of infected mice markedly decreased. Moreover, GRh2 also significantly decreased the T. gondii burden in mouse brain tissues. These findings indicate that GRh2 exhibits an anti-T. gondii effect and inhibits the microglial activation through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, providing the basic pharmacological basis for the development of new drugs to treat toxoplasmic encephalitis.
Keywords: Ginsenoside Rh2; Microglia; TLR4; Toxoplasma gondii; Toxoplasmic encephalitis.
© 2019 The Korean Society of Ginseng, Published by Elsevier Korea LLC.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rh2 against Toxoplasma gondii infection-induced neuronal injury through binding TgCDPK1 and NLRP3 to inhibit microglial NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109176. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109176. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36067653
-
Ginsenoside Rh2 reduces depression in offspring of mice with maternal toxoplasma infection during pregnancy by inhibiting microglial activation via the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ginseng Res. 2022 Jan;46(1):62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35035240 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ginsenoside Rh2-Mix on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells.J Med Food. 2018 Oct;21(10):951-960. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4180. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Med Food. 2018. PMID: 30239266
-
The ways for ginsenoside Rh2 to fight against cancer: the molecular evidences in vitro and in vivo.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Mar;47(2):173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.09.011. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 36926617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer effects and potential mechanisms of ginsenoside Rh2 in various cancer types (Review).Oncol Rep. 2021 Apr;45(4):33. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7984. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649861 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of mitochondrial stress and the NLRP3 inflammasome in lung diseases.Inflamm Res. 2023 Apr;72(4):829-846. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01712-4. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36905430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Re promotes osteogenic differentiation via BMP2/p38 pathway in vivo and in vitro.J Ginseng Res. 2025 Jul;49(4):395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2025.03.003. Epub 2025 Mar 12. J Ginseng Res. 2025. PMID: 40621075 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the Elucidation of the Antinociceptive Effect of Ginseng and Ginsenosides in Chronic Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 21;13:821940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.821940. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35264958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of the HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4/NF-κB signalling pathway in patients with idiopathic epilepsy and its relationship with toxoplasmosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jul;28(14):e18542. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18542. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39046369 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Phellinus baumii Extract on CFA-Induced Inflammation in MH-S Cells through Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 25;2021:5535630. doi: 10.1155/2021/5535630. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34733341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dubey J.P., Jones J.L. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int J Parasitol. 2008;38:1257–1278. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

