Carnosic acid increases sorafenib-induced inhibition of ERK1/2 and STAT3 signaling which contributes to reduced cell proliferation and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 32913557
- PMCID: PMC7443370
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27687
Carnosic acid increases sorafenib-induced inhibition of ERK1/2 and STAT3 signaling which contributes to reduced cell proliferation and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
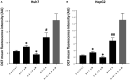
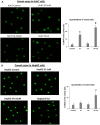
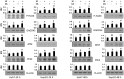
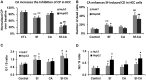
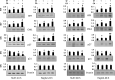
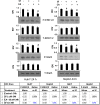
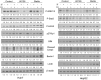
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has increasing worldwide incidence but when unresectable lacks curative options. Treatment with a kinase inhibitor Sorafenib (Sf), while initially effective, results in only short increases in patient survival, thus there is a need for improved treatment regimens. Numerous treatment regimens have been explored wherein Sf is combined with other agents, such as non-toxic botanicals like Curcumin or Silibinin. Recently, we have shown that carnosic acid (CA), a component of the food preservative Rosemary Extract, can markedly enhance the cytotoxic actions of Sf in several cell lines derived from HCC, but not in the cell line Hu1545 derived from normal hepatocytes. CA has been shown to enhance Sf-induced cell death in the neoplastic cell lines, principally due to the composite of increased apoptosis and cytotoxic autophagy. In the present study we focused on the mechanisms that underlie the reduced proliferation and survival of HCC cells when CA is added to Sf and how this relates to the increase in Sf-induced DNA damage as well as to the elevation of cytoplasmic levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Importantly, the elevation of ROS levels induced by Sf was increased by adding CA. We found that CA enhanced Sf-induced prolongation of cell cycle, and the overall decrease in cell growth was associated with reduced activation of both STAT3 transcription factor (TF) and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (Erk)1/2. Our data suggest that a regimen incorporating CA, an inexpensive and non-toxic food additive, in the treatment of advanced HCC merits clinical evaluation.
Keywords: ERK1/2; STAT3; carnosic acid; hepatoma; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancement of sorafenib-mediated death of Hepatocellular carcinoma cells by Carnosic acid and Vitamin D2 analog combination.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;197:105524. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105524. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31704246 Free PMC article.
-
Combined treatment with sorafenib and silibinin synergistically targets both HCC cells and cancer stem cells by enhanced inhibition of the phosphorylation of STAT3/ERK/AKT.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 5;832:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.05.027. Epub 2018 May 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29782854
-
Synergistic antitumor activity of sorafenib and artesunate in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Dec;41(12):1609-1620. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0395-5. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32300243 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib inhibits growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking STAT3.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep 14;17(34):3922-32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22025881 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Etiology and Current and Future Drugs.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Mar-Apr;9(2):221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31024205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adverse Toxic Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Non-Target Zebrafish Liver (ZFL) Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3894. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043894. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835302 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule High-throughput Screening Identifies an MEK Inhibitor PD198306 that Enhances Sorafenib Efficacy via MCL-1 and BIM in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(7):1364-1374. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220830145026. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 36043792 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Crocus sativus L. (saffron) and Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary) in hepatocellular carcinoma: A narrative review of current evidence and prospects.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(8):986-1003. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.84172.18204. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40584445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Mechanisms of Natural Products: Insight from Rosemary Diterpenes, Carnosic Acid and Carnosol.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 13;11(2):545. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020545. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering STAT3 signaling potential in hepatocellular carcinoma: tumorigenesis, treatment resistance, and pharmacological significance.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Apr 21;28(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00438-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37085753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, et al., and SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390. 10.1056/NEJMoa0708857. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abou-Alfa GK, Meyer T, Cheng AL, El-Khoueiry AB, Rimassa L, Ryoo BY, Cicin I, Merle P, Chen Y, Park JW, Blanc JF, Bolondi L, Klumpen HJ, et al., and RESORCE Investigators. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:54–63. 10.1056/NEJMoa1717002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang YH, Bodoky G, Pracht M, Yokosuka O, Rosmorduc O, Breder V, Gerolami R, Masi G, Ross PJ, et al., and RESORCE Investigators. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017; 389:56–66. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32453-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu AX, Kang YK, Yen CJ, Finn RS, Galle PR, Llovet JM, Assenat E, Brandi G, Pracht M, Lim HY, Rau KM, Motomura K, Ohno I, et al., and REACH-2 study investigators. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased alpha-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:282–296. 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30937-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

