Shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures in the elderly: The path from Neer to Grammont
- PMID: 32913595
- PMCID: PMC7459385
- DOI: 10.4081/or.2020.8659
Shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures in the elderly: The path from Neer to Grammont
Abstract
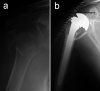
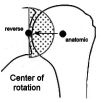
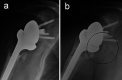
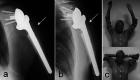
Shoulder replacement is indicated for the surgical treatment of proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients, when severe comminution and osteoporosis jeopardize the chances of success of any fixation technique. Two different implants are available for this purpose: anatomical hemiarthroplasty (HA) and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA). HA for fractures was popularized by Charles Neer in the '50s and for several decades remained the only reliable implant for these injuries. However, many authors reported inconsistent results with HA as a consequence of the high rate of tuberosity and rotator cuff failure. In 1987, Paul Grammont designed the first successful RTSA, which was the end result of a long thought process on functional surgery of the shoulder. This implant was initially used to treat cuff tear arthropathy and shoulder pseudoparalysis, but indications have gradually expanded with time. Since RTSA does not rely on a functional cuff for shoulder elevation, it was felt that results in fractures could be improved by this prosthesis. In this study, the salient features of these implants are described to understand the rationale behind both approaches and highlight their pros and cons. Several clinical studies comparing HA vs RTSA for proximal humeral fractures have been published during the last two decades. A literature review is carried out to analyze and compare outcomes of both implants, analyzing clinical results, radiographic findings and complications. The final goal is to provide an overview of the different factors to consider for making a choice between these two prostheses.
Keywords: elderly; osteoporosis; proximal humeral fractures; reverse shoulder arthroplasty; shoulder hemiarthroplasty.
©Copyright: the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Five-year outcome after conversion of a hemiarthroplasty when used for the treatment of a proximal humeral fracture to a reverse total shoulder arthroplasty.Bone Joint J. 2018 Jun 1;100-B(6):761-766. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B6.BJJ-2017-1280.R1. Bone Joint J. 2018. PMID: 29855243
-
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty compared to stemmed hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: a registry analysis of 5946 patients.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020 Dec;29(12):2538-2547. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020. PMID: 32684280
-
Comparison of hemiarthroplasty and reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Nov 20;95(22):2050-5. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.01637. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013. PMID: 24257664
-
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Biomechanics and Indications.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2019 Dec;12(4):542-553. doi: 10.1007/s12178-019-09586-y. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2019. PMID: 31773478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty for the Treatment of 3 and 4- Part Fractures of the Humeral Head in the Elderly.Open Orthop J. 2017 Feb 28;11:108-118. doi: 10.2174/1874325001711010108. eCollection 2017. Open Orthop J. 2017. PMID: 28400879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Evidence and Surgical Strategies in the Management of Greater Tuberosity Fracture-Dislocations: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 21;14(14):5159. doi: 10.3390/jcm14145159. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prosthetic treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025 May 12;51(1):201. doi: 10.1007/s00068-025-02867-x. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025. PMID: 40353865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The surgical treatment of proximal humerus fractures 2010-2019: United States national case volume and incidence trends.JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023 Mar 31;4(2):146-152. doi: 10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.02.009. eCollection 2024 May. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023. PMID: 38706683 Free PMC article.
-
A unique tribological inverted bearing solution for reverse shoulder arthroplasty: Vitamin E and ceramic (unique inverse pairings in rTSR).Shoulder Elbow. 2024 Jul 23;17(4):450-458. doi: 10.1177/17585732241265627. eCollection 2025 Jul. Shoulder Elbow. 2024. PMID: 39552659 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoporosis Management for Shoulder Surgeons.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2024 Dec;17(12):559-569. doi: 10.1007/s12178-024-09927-6. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2024. PMID: 39276194 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury 2006;37:691-7. - PubMed
-
- Calvo E, Morcillo D, Foruria AM, et al. Nondisplaced proximal humeral fractures: high incidence among outpatient-treated osteoporotic fractures and severe impact on upper extremity function and patient subjective health perception. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011;20:795-801. - PubMed
-
- Murray IR, Amin AK, White TO, Robinson CM. Proximal humeral fractures: current concepts in classification, treatment and outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2011;93:1-11. - PubMed
-
- Piccioli A, Maccauro G, Rossi B, et al. Surgical treatment of pathologic fractures of humerus. Injury. 2010; 41:1112-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

