Pharmacophore-driven identification of N-methyl-D-receptor antagonists as potent neuroprotective agents validated using in vivo studies
- PMID: 32913897
- PMCID: PMC7474860
- DOI: 10.1093/biomethods/bpaa013
Pharmacophore-driven identification of N-methyl-D-receptor antagonists as potent neuroprotective agents validated using in vivo studies
Abstract
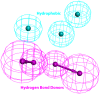
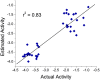
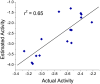
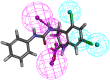
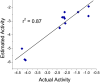
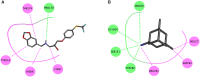
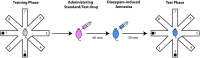
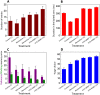
Alzheimer's disease (AD), apparently the most widespread reason behind dementia, is delineated by a continuous cognitive weakening in the aged. During its progression, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonists are known to play a pivotal part in the mechanisms of learning and memory. Since there is an unmet medical need for the treatment of AD, we aim to identify possible chemical compounds targeted toward N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Three-dimensional models are developed to unveil some of the essential characteristics of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by using a collection of already discovered N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor inhibitors. This is followed by virtual screening, which results in novel chemical compounds having the potential to inhibit N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Molecular docking studies and analysis promulgated two lead compounds with a high LibDock score. The compounds are shortlisted based on high estimated activity, fit values, LibDock score, no violation of Lipinski's, and availability for procuring. Finally, the shortlisted compounds are tested by employing in vivo studies, which we further propose as potential NMDA inhibitors for treating AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Discovery Studio; N-methyl-D-aspartate; molecular docking.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Salituro FG, Harrison BL, Baron BM. et al. 3-(2-Carboxyindol-3-yl) propionic acid-based antagonists of the NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartic acid) receptor associated glycine binding site. J Med Chem 1992;35:1791–9. - PubMed
-
- Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M.. NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001;11:327–35. - PubMed
-
- Chenard BL, Menniti FS.. Antagonists selective for NMDA receptors containing the NR2B subunit. Curr Pharm Des 1999;5:381–404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
