Evaluation of Commercial Circulating Tumor DNA Test in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 32914020
- PMCID: PMC7446428
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.19.00014
Evaluation of Commercial Circulating Tumor DNA Test in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) sequencing provides a minimally invasive method for tumor molecular stratification. Commercial ctDNA sequencing is increasingly used in the clinic, but its accuracy in metastatic prostate cancer is untested. We compared the commercial Guardant360 ctDNA test against an academic sequencing approach for profiling metastatic prostate cancer.
Patients and methods: Plasma cell-free DNA was collected between September 2016 and April 2018 from 24 patients with clinically progressive metastatic prostate cancer representing a range of clinical scenarios. Each sample was analyzed using Guardant360 and a research panel encompassing 73 prostate cancer genes. Concordance of somatic mutation and copy number calls was evaluated between the two approaches.
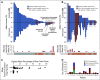
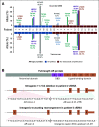
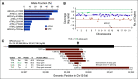
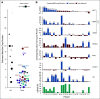
Results: Targeted sequencing independently confirmed 94% of somatic mutations identified by Guardant360 at an allele fraction greater than 1%. AR amplifications and mutations were detected with high concordance in 14 patients, with only three discordant subclonal mutations at an allele fraction lower than 0.5%. Many somatic mutations identified by Guardant360 at an allele fraction lower than 1% seemed to represent subclonal passenger events or non-prostate-derived clones. Most of the non-AR gene amplifications reported by Guardant360 represented single copy gains. The research approach detected several clinically relevant DNA repair gene alterations not reported by Guardant360, including four germline truncating BRCA2/ATM mutations, two somatic ATM stop gain mutations, one BRCA2 biallelic deletion, 11 BRCA2 stop gain reversal mutations in a patient treated with olaparib, and a hypermutator phenotype in a patient sample with 42 mutations per megabase.
Conclusion: Guardant360 accurately identifies somatic ctDNA mutations in patients with metastatic prostate cancer, but low allele frequency mutations should be interpreted with caution. Test utility in metastatic prostate cancer is currently limited by the lack of reporting on actionable deletions, rearrangements, and germline mutations.
© 2019 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/po/author-center.Kim N. ChiHonoraria: Sanofi, Janssen, Astellas Pharma, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Consulting or Advisory Role: ESSA Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Janssen, Sanofi, Eli Lilly/ImClone, Amgen, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Research Funding: Janssen (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Sanofi (Inst), Tokai Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Eli Lilly/ImClone (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck (Inst), Roche (Inst)Oliver SartorStock and Other Ownership Interests: Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Noria Consulting or Advisory Role: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Dendreon, Endocyte, Constellation Pharmaceuticals, Advanced Accelerator Applications, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Bavarian Nordic, Oncogenex, EMD Serono, Astellas Pharma, Progenics, Noria Research Funding: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Johnson & Johnson (Inst), Sanofi (Inst), Endocyte (Inst), Innocrin Pharma (Inst), Merck (Inst), InVitae (Inst), Constellation Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Advanced Accelerator Applications (Inst) Expert Testimony: Sanofi Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, ProgenicsAlexander W. WyattConsulting or Advisory Role: Genzyme Speakers’ Bureau: Janssen Research Funding: Janssen No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guardant360 Circulating Tumor DNA Assay Is Concordant with FoundationOne Next-Generation Sequencing in Detecting Actionable Driver Mutations in Anti-EGFR Naive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.Oncologist. 2020 Mar;25(3):235-243. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0441. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32162812 Free PMC article.
-
Concordance of Circulating Tumor DNA and Matched Metastatic Tissue Biopsy in Prostate Cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017 Dec 1;109(12):djx118. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx118. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017. PMID: 29206995 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of AR Alterations in Circulating Tumor DNA from Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer.Oncologist. 2020 Apr;25(4):327-333. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0115. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32297439 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor DNA Testing for Homology Recombination Repair Genes in Prostate Cancer: From the Lab to the Clinic.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 24;22(11):5522. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115522. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA repair deficiency as circulating biomarker in prostate cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 30;13:1115241. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1115241. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36793600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Role of DNA Damage Response Genes Mutations and their Association With the Sensitivity of Olaparib in Prostate Cancer Patients.Cancer Control. 2022 Jan-Dec;29:10732748221129451. doi: 10.1177/10732748221129451. Cancer Control. 2022. PMID: 36283420 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Obstacles in Liquid Biopsy Developments for Prostate Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2022 Aug 26;15:897-912. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S285758. eCollection 2022. Onco Targets Ther. 2022. PMID: 36051571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic amplifications identified by circulating tumor DNA analysis guide prognosis in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 21;13:1202277. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1202277. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38450313 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment-emergent neuroendocrine prostate cancer with a germline BRCA2 mutation: identification of a candidate reversion mutation associated with platinum/PARP-inhibitor resistance.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2021 Feb 19;7(1):a005801. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a005801. Print 2021 Feb. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2021. PMID: 33608381 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Informed Selection and Interpretation of Clinical Genomic Tests in Prostate Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2024 Mar;8:e2300654. doi: 10.1200/PO.23.00654. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38547422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Annala M, Vandekerkhove G, Khalaf D, et al. Circulating tumor DNA genomics correlate with resistance to abiraterone and enzalutamide in prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:444–457. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran RB, Chabner BA. Application of cell-free DNA analysis to cancer treatment. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1754–1765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

