Application of Circulating Cell-Free Tumor DNA Profiles for Therapeutic Monitoring and Outcome Prediction in Genetically Heterogeneous Metastatic Melanoma
- PMID: 32914028
- PMCID: PMC7446476
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.18.00229
Application of Circulating Cell-Free Tumor DNA Profiles for Therapeutic Monitoring and Outcome Prediction in Genetically Heterogeneous Metastatic Melanoma
Abstract
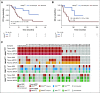
Purpose: Circulating cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA) reflects the heterogeneous spectrum of tumor-specific mutations, especially in systemic disease. We validated plasma-based assays that allow the dynamic quantitative detection of ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker for tumor load and prediction of therapy response in melanoma.
Materials and methods: We analyzed plasma-derived ctDNA from a large training cohort (n = 96) of patients with advanced-stage melanoma, with assays for the BRAF V600E and NRAS Q61 driver mutations as well as TERT C250T and TERT C228T promoter mutations. An independent patient cohort (n = 35) was used to validate the utility of ctDNA monitoring under mitogen-activated protein kinase-targeted or immune checkpoint therapies.
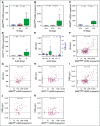
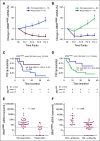
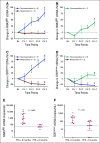
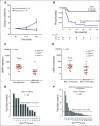
Results: Elevated plasma ctDNA level at baseline was an independent prognostic factor of disease progression when compared with serum S100 and lactate dehydrogenase levels in multivariable analyses (hazard ratio [HR], 7.43; 95% CI, 1.01 to 55.19; P = .05). The change in ctDNA levels during therapy correlated with treatment response, where increasing ctDNA was predictive for shorter progression-free survival (eg, for BRAF V600E ctDNA, HR, 3.70; 95% CI, 1.86 to 7.34; P < .001). Increasing ctDNA levels predicted disease progression significantly earlier than did routine radiologic scans (P < .05), with a mean lead time of 3.5 months. NRAS-mutant ctDNA was detected in a significant proportion of patients with BRAF-mutant tumors under therapy, but unexpectedly also at baseline. In vitro sensitivity studies suggested that this represents higher-than-expected intratumoral heterogeneity. The detection of NRAS Q61 ctDNA in baseline samples of patients with BRAF V600E mutation who were treated with mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors significantly correlated with shorter progression-free survival (HR, 3.18; 95% CI, 1.31 to 7.68; P = .03) and shorter overall survival (HR, 4.08; 95% CI, 1.57 to 10.58; P = .01).
Conclusion: Our results show the potential role of ctDNA measurement as a sensitive monitoring and prediction tool for the early assessment of disease progression and therapeutic response in patients with metastatic melanoma.
© 2019 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/po/author-center. Teofila SeremetEmployment: Janssen (I), GlaxoSmithKline (I) Honoraria: Novartis, Janssen Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis Speakers' Bureau: Novartis Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis, MSD Oncology, Janssen, LEO PharmaKlaus GriewankPatents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Exon 4 mutations in GNAQ and GNA11, a rare gene mutation in melanoma. I receive annual payments. Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: RocheJan-Malte PlackeTravel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol-Myers SquibbPeter A. HornStock and Other Ownership Interests: share certificates (Aktien) of different companies Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Patent applicationsJürgen BeckerConsulting or Advisory Role: Merck Serono, Amgen, eTheRNA, Sanofi/Regeneron Speakers' Bureau: Amgen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Sanofi/Regeneron, Merck Serono (Inst), Alcedis (Inst), IQvia (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: 4SC, Merck SeronoJulia Newton-BishopTravel, Accommodations, Expenses: Unknown mixedBart NeynsHonoraria: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche, Merck Sharp & Dohme Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Amgen Speakers' Bureau: Novartis Research Funding: Pfizer (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Merck KGaA (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche, Merck Sharp & Dohme, AmgenBenjamin WeideHonoraria: Roche, MSD, Bristol-Myers Squibb Consulting or Advisory Role: CureVac, Philogen Research Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), MSD (Inst), Philogen (Inst)Dirk SchadendorfHonoraria: Roche, Novartis, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Sysmex, Immunocore, Grünenthal Group, Merck Serono, Agenus, Array BioPharma, AstraZeneca, LEO Pharma, Incyte, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Philogen, Regeneron, 4SC, Mologen Consulting or Advisory Role: Roche, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck Serono, Amgen, Immunocore, Incyte, 4SC, Pierre Fabre, Mologen, Sanofi/Regeneron Speakers' Bureau: Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Amgen, Incyte, Pierre Fabre Research Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Merck, Merck Serono, NovartisAlexander RoeschHonoraria: Novartis Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis Research Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis (Inst), Adtec (Inst) No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Wong SQ, Raleigh JM, Callahan J, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis and functional imaging provide complementary approaches for comprehensive disease monitoring in metastatic melanoma. JCO Precis Oncol. 2017;1:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Lipson EJ, Velculescu VE, Pritchard TS, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis as a real-time method for monitoring tumor burden in melanoma patients undergoing treatment with immune checkpoint blockade. J Immunother Cancer. 2014;2:42. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25516806 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanmamed MF, Fernández-Landázuri S, Rodríguez C, et al. Quantitative cell-free circulating BRAFV600E mutation analysis by use of droplet digital PCR in the follow-up of patients with melanoma being treated with BRAF inhibitors. Clin Chem. 2015;61:297–304. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25411185 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

