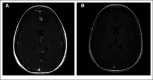
Dramatic Response to Lorlatinib in a Patient With CD74-ROS1-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma With Acquired F2004V Mutation
- PMID: 32914039
- PMCID: PMC7450917
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.19.00013
Dramatic Response to Lorlatinib in a Patient With CD74-ROS1-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma With Acquired F2004V Mutation
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/po/author-center. Sai-Hong I. OuStock and Other Ownership Interests: Turning Point Therapeutics Honoraria: Pfizer, Roche Pharma AG, Roche, ARIAD/Takeda, AstraZeneca, Foundation Medicine, Merck Consulting or Advisory Role: Pfizer, Roche, AstraZeneca, Takeda, Foundation Medicine, Turning Point Therapeutics, Ignyta Speakers' Bureau: Genentech, AstraZeneca, Takeda Research Funding: Pfizer (Inst), Roche Pharma AG (Inst), AstraZeneca/MedImmune (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), ARIAD (Inst), Ignyta (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Chugai Pharma (Inst), Revolution Medicines (Inst)Robert C. DoebeleStock and Other Ownership Interests: Rain Therapeutics Consulting or Advisory Role: OncoMed, Ignyta, GreenPeptide, AstraZeneca, Roche, Bayer, Takeda, Rain Therapeutics Research Funding: Ignyta (Inst) Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Licensing fees from Abbott Molecular for Patent PCT/US2013/057495, licensing fees from Ignyta for biologic materials (Inst), licensing fees for biologic materials from Genentech (Inst), licensing fees for patent from Rain Therapeutics Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Ignyta, Rain Therapeutics, Roche No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

