Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS
- PMID: 32914148
- PMCID: PMC7480905
- DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.1.013
Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS
Abstract
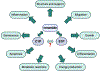
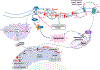
Sphingolipids are well-recognized as major players in the pathogenesis of many human diseases, including chronic kidney disease. The kidney is a very sensitive organ to alterations in sphingolipid metabolism. The critical issues to be addressed in this review relate to the role of sphingolipids and enzymes involved in sphingolipid metabolism in the pathogenesis of glomerular diseases with a special focus on podocytes, a key cellular component of the glomerular filtration barrier. Among several sphingolipids, we will highlight the role of ceramide, sphingosine, sphingosine-1-phosphate and ceramide-1-phosphate. Additionally, we will summarize the current knowledge with regard to the use of sphingolipids as therapeutic agents for the treatment of podocyte injury in kidney disease.
Keywords: C1P; Ceramide; DKD; FSGS; Kidney; Podocyte; S1P; SMPDL3b; Sphingolipids.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest A.F. and S.M. are inventors on pending or issued patents (PCT/US11/56272, PCT/US12/62594, PCT/ US2019/041730, PCT/US2019/032215, PCT/US13/36484 and PCT 62/674,897) aimed to diagnosing or treating proteinuric kidney diseases. They stand to gain royalties from their future commercialization of these patents. A.F. is Vice-President of L&F Health LLC and is consultant for ZyVersa Therapeutics, Inc. ZyVersa Therapeutics, Inc has licensed worldwide rights to develop and commercialize hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin from L&F Research for the treatment of kidney disease. A.F. is founder of LipoNexT LLC. S.M. is a consultant for Kintai Therapeutics, Inc and holds equity interest in L&F Research. AF and SM are supported by Boehringer Ingelheim. AM and YD declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Podocyte pathology and nephropathy - sphingolipids in glomerular diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Jul 30;5:127. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00127. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25126087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normal and Dysregulated Sphingolipid Metabolism: Contributions to Podocyte Injury and Beyond.Cells. 2024 May 22;13(11):890. doi: 10.3390/cells13110890. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Metabolism and Signaling in Kidney Diseases.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jan;32(1):9-31. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020050697. Epub 2020 Dec 18. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33376112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid mediators of insulin signaling in diabetic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):F1241-F1252. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00379.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31545927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the amount of ceramide-1-phosphate synthesized in differentiated human podocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019 Dec;1864(12):158517. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158517. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019. PMID: 31487557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rotten to the Cortex: Ceramide-Mediated Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 28;11:622692. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.622692. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33584550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRB2 depletion induces YAP signaling and disrupts mechanosensing in podocytes.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Apr 1;328(4):F578-F595. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00318.2024. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40062402 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic-reticulum-stress-induced lipotoxicity in human kidney epithelial cells.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2022 Jul 22;11(4):683-695. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfac041. eCollection 2022 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36051659 Free PMC article.
-
The Updates of Podocyte Lipid Metabolism in Proteinuric Kidney Disease.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2021 Sep 1;7(6):438-451. doi: 10.1159/000518132. eCollection 2021 Nov. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34901191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles metabolic changes reveals plasma signature in stage-dependent diabetic kidney disease.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):1840-1849. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2118067. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 36368309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- USRDS. US Renal Data System 2019 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Minneapolis, MN: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2019.
-
- Bjercke O The Norwegian Medical Association as it is. Tidsskrift for den Norske laegeforening: tidsskrift for praktisk medicin, ny raekke. 1970. May 30;90(106):Suppl-1180. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
