α-Functionalisation of Ketones Through Metal-Free Electrophilic Activation
- PMID: 32914929
- PMCID: PMC7693173
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202006398
α-Functionalisation of Ketones Through Metal-Free Electrophilic Activation
Abstract
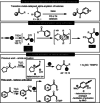
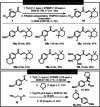
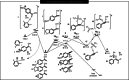
Triflic anhydride mediated activation of acetophenones leads to highly electrophilic intermediates that can undergo a variety of transformations when treated with nucleophiles. This electrophilic ketone activation gives access to α-arylated and α-oxyaminated acetophenones under metal-free conditions in moderate to excellent yields and enables extension to the synthesis of arylated morpholines via generation of vinylsulfonium salts. Computational investigations confirmed the transient existence of intermediates derived from vinyl triflates and the role of the oxygen atoms at the para position of aromatic ring in facilitating their stabilisation.
Keywords: sigmatropic rearrangement; vinyl cations; vinyl triflate; α-arylation; α-oxyamination.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vinyl Cation Stabilization by Silicon Enables a Formal Metal-Free α-Arylation of Alkyl Ketones.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Nov 25;58(48):17303-17306. doi: 10.1002/anie.201909381. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31638738 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric Catalytic Rearrangements with α-Diazocarbonyl Compounds.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Feb 1;55(3):415-428. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00664. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 35029358
-
Direct synthesis of phenanthrenyl triflates from 1-biphenylyl-2-diazo-2-aryl ketones and triflic anhydride.Org Biomol Chem. 2024 Feb 7;22(6):1141-1145. doi: 10.1039/d3ob02005c. Org Biomol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38214226
-
Cascades of Interrupted Pummerer Reaction-Sigmatropic Rearrangement.Chem Rec. 2017 Nov;17(11):1156-1167. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201700017. Epub 2017 May 10. Chem Rec. 2017. PMID: 28488753 Review.
-
From α-arylation of olefins to acylation with aldehydes: a journey in regiocontrol of the Heck reaction.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Aug 16;44(8):614-26. doi: 10.1021/ar200053d. Epub 2011 May 25. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21612205 Review.
Cited by
-
Free Amino Group Transfer via α-Amination of Native Carbonyls.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023 Jul 10;62(28):e202304990. doi: 10.1002/anie.202304990. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023. PMID: 37114555 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer freier Aminogruppen via α-Aminierung von Carbonylen.Angew Chem Weinheim Bergstr Ger. 2023 Jul 10;135(28):e202304990. doi: 10.1002/ange.202304990. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Angew Chem Weinheim Bergstr Ger. 2023. PMID: 38516250 Free PMC article.
-
Formal Enone α-Arylation via I(III)-Mediated Aryl Migration/Elimination.Org Lett. 2021 Mar 19;23(6):2094-2098. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00251. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Org Lett. 2021. PMID: 33635665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- None
-
- Johansson C. C. C., Colacot T. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 676–707; - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 686–718;
-
- Li J., Wang Z. X., Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 7579–7584; - PubMed
-
- Satoh T., Kawamura Y., Miura M., Nomura M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 1740–1742;
- Angew. Chem. 1997, 109, 1820–1822;
-
- Palucki M., Buchwald S. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11108–11109;
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

