Optimization of a Bayesian penalized likelihood algorithm (Q.Clear) for 18F-NaF bone PET/CT images acquired over shorter durations using a custom-designed phantom
- PMID: 32915344
- PMCID: PMC7486353
- DOI: 10.1186/s40658-020-00325-8
Optimization of a Bayesian penalized likelihood algorithm (Q.Clear) for 18F-NaF bone PET/CT images acquired over shorter durations using a custom-designed phantom
Abstract
Background: The Bayesian penalized likelihood (BPL) algorithm Q.Clear (GE Healthcare) allows fully convergent iterative reconstruction that results in better image quality and quantitative accuracy, while limiting image noise. The present study aimed to optimize BPL reconstruction parameters for 18F-NaF PET/CT images and to determine the feasibility of 18F-NaF PET/CT image acquisition over shorter durations in clinical practice.
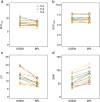
Methods: A custom-designed thoracic spine phantom consisting of several inserts, soft tissue, normal spine, and metastatic bone tumor, was scanned using a Discovery MI PET/CT scanner (GE Healthcare). The phantom allows optional adjustment of activity distribution, tumor size, and attenuation. We reconstructed PET images using OSEM + PSF + TOF (2 iterations, 17 subsets, and a 4-mm Gaussian filter), BPL + TOF (β = 200 to 700), and scan durations of 30-120 s. Signal-to-noise ratios (SNR), contrast, and coefficients of variance (CV) as image quality indicators were calculated, whereas the quantitative measures were recovery coefficients (RC) and RC linearity over a range of activity. We retrospectively analyzed images from five persons without bone metastases (male, n = 1; female, n = 4), then standardized uptake values (SUV), CV, and SNR at the 4th, 5th, and 6th thoracic vertebra were calculated in BPL + TOF (β = 400) images.
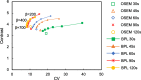
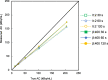
Results: The optimal reconstruction parameter of the BPL was β = 400 when images were acquired at 120 s/bed. At 90 s/bed, the BPL with a β value of 400 yielded 24% and 18% higher SNR and contrast, respectively, than OSEM (2 iterations; 120 s acquisitions). The BPL was superior to OSEM in terms of RC and the RC linearity over a range of activity, regardless of scan duration. The SUVmax were lower in BPL, than in OSEM. The CV and vertebral SNR in BPL were superior to those in OSEM.
Conclusions: The optimal reconstruction parameters of 18F-NaF PET/CT images acquired over different durations were determined. The BPL can reduce PET acquisition to 90 s/bed in 18F-NaF PET/CT imaging. Our results suggest that BPL (β = 400) on SiPM-based TOF PET/CT scanner maintained high image quality and quantitative accuracy even for shorter acquisition durations.
Keywords: 18F-NaF; BPL; Q.Clear; Quantitation; SiPM; TOF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Detection of sub-centimeter lesions using digital TOF-PET/CT system combined with Bayesian penalized likelihood reconstruction algorithm.Ann Nucl Med. 2020 Oct;34(10):762-771. doi: 10.1007/s12149-020-01500-8. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Ann Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32623569
-
Determination of optimal regularization factor in Bayesian penalized likelihood reconstruction of brain PET images using [18 F]FDG and [11 C]PiB.Med Phys. 2022 May;49(5):2995-3005. doi: 10.1002/mp.15593. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 35246870
-
The value of Bayesian penalized likelihood reconstruction for improving lesion conspicuity of malignant lung tumors on 18F-FDG PET/CT: comparison with ordered subset expectation maximization reconstruction incorporating time-of-flight model and point spread function correction.Ann Nucl Med. 2020 Apr;34(4):272-279. doi: 10.1007/s12149-020-01446-x. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Ann Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32060780
-
18F-NaF PET/CT of Obese Patients on a Lutetium-Yttrium Oxyorthosilicate PET/CT System: Patient Dosimetry, Optimization of Injected Activity, and Acquisition Time.J Nucl Med Technol. 2021 Jun;49(2):150-155. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.120.258137. Epub 2020 Dec 30. J Nucl Med Technol. 2021. PMID: 33380519 Review.
-
The SwiftScan step-and-shoot continuous mode improves SPECT scanning efficiency: a preliminary phantom and clinical test.EJNMMI Phys. 2025 Jan 2;12(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40658-024-00709-0. EJNMMI Phys. 2025. PMID: 39745654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New PET technologies - embracing progress and pushing the limits.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Aug;48(9):2711-2726. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05390-4. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34081153 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Innovations in clinical PET image reconstruction: advances in Bayesian penalized likelihood algorithm and deep learning.Ann Nucl Med. 2025 Sep;39(9):875-898. doi: 10.1007/s12149-025-02088-7. Epub 2025 Jul 18. Ann Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40681770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of dynamic [18F]NaF PET scan duration on kinetic uptake parameters in the knee.Front Nucl Med. 2023 Nov 24;3:1194961. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2023.1194961. eCollection 2023. Front Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 39355034 Free PMC article.
-
Phantom and clinical evaluation of the Bayesian penalised likelihood reconstruction algorithm Q.Clear without PSF correction in amyloid PET images.EJNMMI Phys. 2024 Apr 22;11(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40658-024-00641-3. EJNMMI Phys. 2024. PMID: 38647924 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of γ factor in the penalty function of Bayesian penalized likelihood reconstruction (Q.Clear) to achieve high-resolution PET images.EJNMMI Phys. 2023 Jan 22;10(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40658-023-00527-w. EJNMMI Phys. 2023. PMID: 36681994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evangelista L, Bertoldo F, Boccardo F, Conti G, Menchi I, Mungai F, et al. Diagnostic imaging to detect and evaluate response to therapy in bone metastases from prostate cancer: current modalities and new horizons. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:1546–1562. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3350-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Segall G, Delbeke D, Stabin MG, Even-Sapir E, Fair J, Sajdak R, et al. SNM practice guideline for sodium 18F-fluoride PET/CT bone scans 1.0. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1813-1820. doi:10.2967/jnumed.110.082263. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

