Regeneration enhanced in critical-sized bone defects using bone-specific extracellular matrix protein
- PMID: 32915522
- PMCID: PMC8740960
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34722
Regeneration enhanced in critical-sized bone defects using bone-specific extracellular matrix protein
Abstract
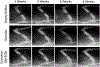
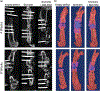
Extracellular matrix (ECM) products have the potential to improve cellular attachment and promote tissue-specific development by mimicking the native cellular niche. In this study, the therapeutic efficacy of an ECM substratum produced by bone marrow stem cells (BM-MSCs) to promote bone regeneration in vitro and in vivo were evaluated. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis and phenotypic expression were employed to characterize the in vitro BM-MSC response to bone marrow specific ECM (BM-ECM). BM-ECM encouraged cell proliferation and stemness maintenance. The efficacy of BM-ECM as an adjuvant in promoting bone regeneration was evaluated in an orthotopic, segmental critical-sized bone defect in the rat femur over 8 weeks. The groups evaluated were either untreated (negative control); packed with calcium phosphate granules or granules+BM-ECM free protein and stabilized by collagenous membrane. Bone regeneration in vivo was analyzed using microcomputed tomography and histology. in vivo results demonstrated improvements in mineralization, osteogenesis, and tissue infiltration (114 ± 15% increase) in the BM-ECM complex group from 4 to 8 weeks compared to mineral granules only (45 ± 21% increase). Histological observations suggested direct apposition of early bone after 4 weeks and mineral consolidation after 8 weeks implantation for the group supplemented with BM-ECM. Significant osteoid formation and greater functional bone formation (polar moment of inertia was 71 ± 0.2 mm4 with BM-ECM supplementation compared to 48 ± 0.2 mm4 in untreated defects) validated in vivo indicated support of osteoconductivity and increased defect site cellularity. In conclusion, these results suggest that BM-ECM free protein is potentially a therapeutic supplement for stemness maintenance and sustaining osteogenesis.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
R. Z. (previously) and S. G. (still) were/are paid employees of StemBioSys, which donated the BM-ECM product tested in this manuscript. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

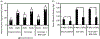
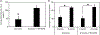

References
-
- Tang D, Tare RS, Yang L-Y, Williams DF, Ou K-L, Oreffo RO. Bio-fabrication of bone tissue: approaches, challenges and translation for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;83:363–382. - PubMed
-
- Castellani C, Zanoni G, Tangl S, Van Griensven M, Redl H. Biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics in small bone defects: potential influence of carrier substances and bone marrow on bone regeneration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20:1367–1374. - PubMed
-
- Turunen T, Peltola J, Yli-Urpo A, Happonen RP. Bioactive glass granules as a bone adjunctive material in maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15:135–141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

