Novel genes associated with folic acid-mediated metabolism in mouse: A bioinformatics study
- PMID: 32915913
- PMCID: PMC7485790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238940
Novel genes associated with folic acid-mediated metabolism in mouse: A bioinformatics study
Abstract
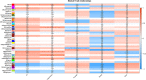
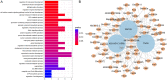
Folic acid plays an essential role in the central nervous system and cancer. This study aimed to screen genes related to folic acid metabolism. Datasets (GSE80587, GSE65267 and GSE116299) correlated to folic acid were screened in the Gene Expression Omnibus. Weighed gene co-expression network analysis was performed to identify modules associated with sample traits of folic acid and organs (brain, prostate and kidney). Functional enrichment analysis was performed for the eigengenes in modules that were significantly correlated with sample traits. Accordingly, the hub genes and key nodes in the modules were identified using the protein interaction network. A total of 17,252 genes in three datasets were identified. One module, which included 97 genes that were highly correlated with sample traits (including folic acid treatment [cor = -0.57, P = 3e-04] and kidney [cor = -0.68, p = 4e-06]), was screened out. Hub genes, including tetratricopeptide repeat protein 38 (Ttc38) and miR-185, as well as those (including Sema3A, Insl3, Dll1, Msh4 and Snai1) associated with "neuropilin binding", "regulation of reproductive process" and "vitamin D metabolic process", were identified. Genes, including Ttc38, Sema3A, Insl3, Dll1, Msh4 and Snai1, were the novel factors that may be associated with the development of the kidneys and related to folic acid treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identifying the key genes and microRNAs in colorectal cancer liver metastasis by bioinformatics analysis and in vitro experiments.Oncol Rep. 2019 Jan;41(1):279-291. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6840. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30542696 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for the screening of hub genes and therapeutic drugs in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2020 Jan 27;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-0613-2. J Ovarian Res. 2020. PMID: 31987036 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression network analysis identified hub genes critical to triglyceride and free fatty acid metabolism as key regulators of age-related vascular dysfunction in mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Sep 12;11(18):7620-7638. doi: 10.18632/aging.102275. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31514170 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling and bioinformatics analysis of gastric carcinoma.Exp Mol Pathol. 2014 Jun;96(3):361-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2014.02.007. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24589858
-
In silico identification of key genes and signaling pathways targeted by a panel of signature microRNAs in prostate cancer.Med Oncol. 2019 Apr 1;36(5):43. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1268-y. Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30937635
Cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes in nulliparas.Sci Rep. 2024 May 7;14(1):10514. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61218-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38714721 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-Wide Discovery of Cortical Proteins That May Provide Motor Resilience to Offset the Negative Effects of Pathologies in Older Adults.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023 Mar 1;78(3):494-503. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glac105. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 35512265 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis and a Call for Increased Rigor in Citing Scientific Literature: Folic Acid Fortification and Neural Tube Defect Risk as an Example.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 1;16(15):2503. doi: 10.3390/nu16152503. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burr NE, Hull MA, Subramanian V. Folic acid supplementation may reduce colorectal cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of clinical gastroenterology. 2017; 51(3): 247–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

