Proximal tubular dysfunction in patients with COVID-19: what have we learnt so far?
- PMID: 32916178
- PMCID: PMC7480737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.002
Proximal tubular dysfunction in patients with COVID-19: what have we learnt so far?
Abstract
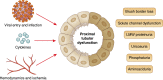
Recent studies have reported a variety of urine abnormalities in patients hospitalized due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. In a single-center study from Belgium, Werion et al. present a concise investigation of tubular dysfunction in patients with coronavirus disease 2019, identifying potential risk factors for increased disease severity. These data complement current evidence regarding severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 presence and potential infection in the kidney.
Copyright © 2020 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment on
-
SARS-CoV-2 causes a specific dysfunction of the kidney proximal tubule.Kidney Int. 2020 Nov;98(5):1296-1307. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.07.019. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32791255 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

