Current Policies and Measures on the Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China
- PMID: 32916255
- PMCID: PMC7480280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105187
Current Policies and Measures on the Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China
Abstract
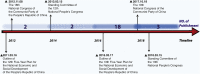
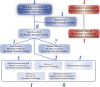
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a medical science and cultural heritage empirically applied and reserved by Chinese people for thousands of years. With comprehensive prosperity of China and rapid elaboration of technology, healthcare status of Chinese people has become one of the most crucial concerns of the country. Nearly 30 policies and measures regarding TCM development have been issued since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of People's Republic of China in 2012. This review introduced a detailed evolutionary course of TCM in China with an emphasis on understanding the roadmap of TCM related policies and measures in China.
Keywords: China; Policies and Measures; Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Liu Ruiche. All the mobile cabin hospitals in Wuhan are equipped with TCM experts. Chang. Dly. 2020 http://news.cctv.com/2020/03/04/ARTIrXzpEsYplXUB0LhdVA70200304.shtml
-
- Hu K., Guan W., Bi Y., Zhang W., Li L., Zhang B., Liu Q., Song Y., Li X., Duan Z., Zheng Q., Yang Z., Liang J., Han M., Ruan L., Wu C., Zhang Y., Jia Z., Zhong N. Efficacy and safety of Lianhuaqingwen capsules, a repurposed Chinese herb, in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial. Phytomedicine. 2020:153242. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153242. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

