The role of Langerhans cells in epidermal homeostasis and pathogenesis of psoriasis
- PMID: 32916775
- PMCID: PMC7579693
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15834
The role of Langerhans cells in epidermal homeostasis and pathogenesis of psoriasis
Abstract
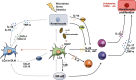
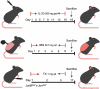
The skin is the main barrier between the human body and the outside world, which not only plays the role of a physical barrier but also functions as the first line of defence of immunology. Langerhans cells (LCs), as dendritic cells (DC) that play an important role in the immune system, are mainly distributed in the epidermis. This review focuses on the role of these epidermal LCs in regulating skin threats (such as microorganisms, ultraviolet radiation and allergens), especially psoriasis. Since human and mouse skin DC subsets share common ontogenetic characteristics, we can further explore the role of LCs in psoriatic inflammation.
Keywords: Langerhans cells; epidermal homeostasis; inflammatory responses; psoriasis.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370(9583):263‐271. - PubMed
-
- Mekori YA, Hershko AY, Frossi B, Mion F, Pucillo CE. Integrating innate and adaptive immune cells: mast cells as crossroads between regulatory and effector B and T cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;778:84‐89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

