The Role of Lipid Environment in Ganglioside GM1-Induced Amyloid β Aggregation
- PMID: 32916822
- PMCID: PMC7558528
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes10090226
The Role of Lipid Environment in Ganglioside GM1-Induced Amyloid β Aggregation
Abstract
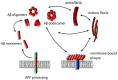
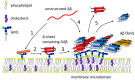
Ganglioside GM1 is the most common brain ganglioside enriched in plasma membrane regions known as lipid rafts or membrane microdomains. GM1 participates in many modulatory and communication functions associated with the development, differentiation, and protection of neuronal tissue. It has, however, been demonstrated that GM1 plays a negative role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The two features of AD are the formation of intracellular neurofibrillary bodies and the accumulation of extracellular amyloid β (Aβ). Aβ is a peptide characterized by intrinsic conformational flexibility. Depending on its partners, Aβ can adopt different spatial arrangements. GM1 has been shown to induce specific changes in the spatial organization of Aβ, which lead to enhanced peptide accumulation and deleterious effect especially on neuronal membranes containing clusters of this ganglioside. Changes in GM1 levels and distribution during the development of AD may contribute to the aggravation of the disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GM1; amyloid oligomers; amyloid β; fibrils; gangliosides; membrane microdomains.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How do membranes initiate Alzheimer's Disease? Formation of toxic amyloid fibrils by the amyloid β-protein on ganglioside clusters.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Aug 19;47(8):2397-404. doi: 10.1021/ar500127z. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25029558
-
Interactions of amyloid beta-protein with various gangliosides in raft-like membranes: importance of GM1 ganglioside-bound form as an endogenous seed for Alzheimer amyloid.Biochemistry. 2002 Jun 11;41(23):7385-90. doi: 10.1021/bi0255874. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12044171
-
Formation of toxic Abeta(1-40) fibrils on GM1 ganglioside-containing membranes mimicking lipid rafts: polymorphisms in Abeta(1-40) fibrils.J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 17;382(4):1066-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.07.072. Epub 2008 Jul 30. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18692507
-
Role of ganglioside metabolism in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease--a review.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jun;49(6):1157-75. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800007-JLR200. Epub 2008 Mar 11. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18334715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aβ-ganglioside interactions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Aug 1;1862(8):183233. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183233. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32142821 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of the Lipid Landscape on the Efficacy of Cell-Penetrating Peptides.Cells. 2023 Jun 23;12(13):1700. doi: 10.3390/cells12131700. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetramodal Chemical Imaging Delineates the Lipid-Amyloid Peptide Interplay at Single Plaques in Transgenic Alzheimer's Disease Models.Anal Chem. 2023 Mar 14;95(10):4692-4702. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05302. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36856542 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol as a key player in amyloid β-mediated toxicity in Alzheimer's disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Aug 25;15:937056. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.937056. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36090253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Mechanism of S. baicalensis on Lipid Metabolism Explored via Network Pharmacology and Untargeted Lipidomics.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 May 4;15:1915-1930. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S301679. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33976541 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Sialylation Status and Cell Susceptibility to Amyloid Toxicity.Cells. 2022 Feb 9;11(4):601. doi: 10.3390/cells11040601. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1545–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jan A., Adolfsson O., Allaman I., Buccarello A.L., Magistretti P.J., Pfeifer A., Muhs A., Lashuel H.A. Abeta42 neurotoxicity is mediated by ongoing nucleated polymerization process rather than by discrete Abeta42 species. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:8585–8596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.172411. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Villemagne V.L., Burnham S., Bourgeat P., Brown B., Ellis K.A., Salvado O., Szoeke C., Macaulay S.L., Martins R., Maruff P., et al. Amyloid beta deposition, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:357–367. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70044-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

