Berberine-Loaded Liposomes for the Treatment of Leishmania infantum-Infected BALB/c Mice
- PMID: 32916948
- PMCID: PMC7558179
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12090858
Berberine-Loaded Liposomes for the Treatment of Leishmania infantum-Infected BALB/c Mice
Abstract
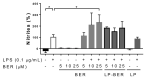
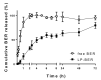
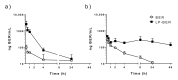
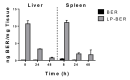
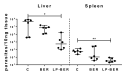
Berberine (BER)-an anti-inflammatory quaternary isoquinoline alkaloid extracted from plants-has been reported to have a variety of biologic properties, including antileishmanial activity. This work addresses the preparation of BER-loaded liposomes with the aim to prevent its rapid liver metabolism and improve the drug selective delivery to the infected organs in visceral leishmaniasis (VL). BER liposomes (LP-BER) displayed a mean size of 120 nm, negative Z-potential of -38 mV and loaded 6 nmol/μmol lipid. In vitro, the loading of BER in liposomes enhanced its selectivity index more than 7-fold by decreasing its cytotoxicity to macrophages. In mice, LP-BER enhanced drug accumulation in the liver and the spleen. Consequently, the liposomal delivery of the drug reduced parasite burden in the liver and spleen by three and one logarithms (99.2 and 93.5%), whereas the free drug only decreased the infection in the liver by 1-log. The organ drug concentrations-far from IC50 values- indicate that BER immunomodulatory activity or drug metabolites also contribute to the efficacy. Although LP-BER decreased 10-fold-an extremely rapid clearance of the free drug in mice-the value remains very high. Moreover, LP-BER reduced plasma triglycerides levels.
Keywords: Leishmania infantum; berberine; liposomes; visceral leishmaniasis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetic of meglumine antimoniate encapsulated in phosphatidylserine-liposomes in mice model: A candidate formulation for visceral leishmaniasis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:1609-1616. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29864949
-
Sertraline Delivered in Phosphatidylserine Liposomes Is Effective in an Experimental Model of Visceral Leishmaniasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 29;9:353. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00353. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31737574 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of liposomal buparvaquone in an experimental hamster model of Leishmania (L.) infantum chagasi.Exp Parasitol. 2012 Mar;130(3):195-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2012.01.010. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Exp Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22281156
-
Nanoliposomal Buparvaquone Immunomodulates Leishmania infantum-Infected Macrophages and Is Highly Effective in a Murine Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Mar 24;61(4):e02297-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02297-16. Print 2017 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28167544 Free PMC article.
-
Hemisynthetic trifluralin analogues incorporated in liposomes for the treatment of leishmanial infections.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:346-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.04.018. Epub 2015 May 1. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25936854
Cited by
-
Berberine-induced browning and energy metabolism: mechanisms and implications.PeerJ. 2025 Feb 7;13:e18924. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18924. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39931072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Applications of Plant-Based Drug Delivery Nano Systems for Leishmaniasis Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 29;14(11):2339. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112339. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of liposomal nanoparticles of berberine in photodynamic therapy of A549 lung cancer spheroids.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Nov 17;40:101877. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101877. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39634336 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Antitumor Activity of Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17237. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417237. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139066 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Validation of Lmj_04_BRCT Domain, a Novel Therapeutic Target: Identification of Candidate Drugs for Leishmaniasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10493. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910493. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ponte-Sucre A., Gamarro F., Dujardin J.-C., Barrett M.P., Lopez-Vélez R., García-Hernández R., Pountain A.W., Mwenechanya R., Papadopoulou B. Drug resistance and treatment failure in leishmaniasis: A 21st century challenge. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017;11:e0006052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

