Comparison of High- and Low-LET Radiation-Induced DNA Double-Strand Break Processing in Living Cells
- PMID: 32917044
- PMCID: PMC7555951
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21186602
Comparison of High- and Low-LET Radiation-Induced DNA Double-Strand Break Processing in Living Cells
Abstract
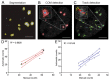
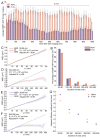
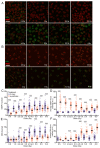
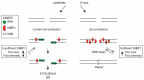
High-linear-energy-transfer (LET) radiation is more lethal than similar doses of low-LET radiation types, probably a result of the condensed energy deposition pattern of high-LET radiation. Here, we compare high-LET α-particle to low-LET X-ray irradiation and monitor double-strand break (DSB) processing. Live-cell microscopy was used to monitor DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), marked by p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1). In addition, the accumulation of the endogenous 53BP1 and replication protein A (RPA) DSB processing proteins was analyzed by immunofluorescence. In contrast to α-particle-induced 53BP1 foci, X-ray-induced foci were resolved quickly and more dynamically as they showed an increase in 53BP1 protein accumulation and size. In addition, the number of individual 53BP1 and RPA foci was higher after X-ray irradiation, while focus intensity was higher after α-particle irradiation. Interestingly, 53BP1 foci induced by α-particles contained multiple RPA foci, suggesting multiple individual resection events, which was not observed after X-ray irradiation. We conclude that high-LET α-particles cause closely interspaced DSBs leading to high local concentrations of repair proteins. Our results point toward a change in DNA damage processing toward DNA end-resection and homologous recombination, possibly due to the depletion of soluble protein in the nucleoplasm. The combination of closely interspaced DSBs and perturbed DNA damage processing could be an explanation for the increased relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET α-particles compared to X-ray irradiation.
Keywords: DNA double-strand breaks; alpha particles; high linear energy transfer; homologous recombination; live-cell microscopy; nonhomologous DNA end-joining.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relative biological effectiveness of high linear energy transfer α-particles for the induction of DNA-double-strand breaks, chromosome aberrations and reproductive cell death in SW-1573 lung tumour cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 Mar;27(3):769-74. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1604. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22200791
-
Most DNA repair defects do not modify the relationship between relative biological effectiveness and linear energy transfer in CRISPR-edited cells.Med Phys. 2024 Jan;51(1):591-600. doi: 10.1002/mp.16764. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 37753877
-
Nanoscale analysis of clustered DNA damage after high-LET irradiation by quantitative electron microscopy--the heavy burden to repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Apr;28:93-106. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 28. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25659339
-
DNA Damage Clustering after Ionizing Radiation and Consequences in the Processing of Chromatin Breaks.Molecules. 2022 Feb 24;27(5):1540. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051540. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clustered DNA double-strand break formation and the repair pathway following heavy-ion irradiation.J Radiat Res. 2019 Jan 1;60(1):69-79. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rry096. J Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 30476166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Taking the 3Rs to a higher level: replacement and reduction of animal testing in life sciences in space research.Biotechnol Adv. 2025 Jul-Aug;81:108574. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2025.108574. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Biotechnol Adv. 2025. PMID: 40180136 Review.
-
Topological Analysis of γH2AX and MRE11 Clusters Detected by Localization Microscopy during X-ray-Induced DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;13(21):5561. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215561. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771723 Free PMC article.
-
Ionization detail parameters and cluster dose: a mathematical model for selection of nanodosimetric quantities for use in treatment planning in charged particle radiotherapy.Phys Med Biol. 2023 Aug 14;68(17):10.1088/1361-6560/acea16. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/acea16. Phys Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37489619 Free PMC article.
-
Development of [225Ac]Ac-DOTA-C595 as radioimmunotherapy of pancreatic cancer: in vitro evaluation, dosimetric assessment and detector calibration.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2023 Sep 7;8(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s41181-023-00209-z. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2023. PMID: 37679594 Free PMC article.
-
The order of sequential exposure of U2OS cells to gamma and alpha radiation influences the formation and decay dynamics of NBS1 foci.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 12;18(6):e0286902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286902. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37307266 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

