Effect of renal replacement therapy on selected arachidonic acid derivatives concentration
- PMID: 32917166
- PMCID: PMC7488457
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-020-02053-8
Effect of renal replacement therapy on selected arachidonic acid derivatives concentration
Abstract
Background: Platelet activation is an important side effect of dialysis, resulted in a subsequent release of arachidonic acid (AA) from activated platelets. AA is involved in many pathologic conditions, such as inflammation, asthma, cancer, diabetes, hypertension, and the pathogenesis of kidney disease. The aim of this study was to define whether the dialysis type affects the concentration of AA derivatives in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Methods: 117 patients were qualified to the study group. Based on the type of renal replacement therapy, patients were divided into the following groups: hemodialysis (HD A - before/HD B - after hemodialysis), peritoneal dialysis (PD), kidney transplant patients (TE - before/TE A - after transplantation) and conservative treatment (CT) (30; 30; 27; 30 patients, respectively). The control group consisted of 30 healthy volunteers (NK). The ELISA methods were used to measure the concentrations of TXB2, 5-HETE, 12-HETE, and 15-HETE in the blood serum.
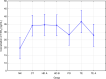
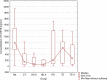
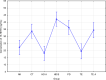
Results: Renal replacement therapy significantly influences the concentration of TXB2 (mean ± SD [ng/mL]: HD A- 34.6 ± 9; HD B- 28.3 ± 15.2; PD- 28.3 ± 15.2; CT- 34.2 ± 8.0; TE- 36.7 ± 42.9; TE A- 27.9 ± 8.8; NK- 19.6 ± 15; p = 0.010), 5-HETE (mean ± SD [ng/mL]: HD A- 284.2 ± 428.4; HD B- 304.8 ± 516.2; PD - 530.0 ± 553.3; CT- 318.7 ± 366.0; TE- 525.6 ± 358.0; TE A - 409.8 ± 377.1; NK 838.1 ± 497.8; p < 0.001) and 15-HETE (HD A-18.1 ± 8.7; HD B- 42.2 ± 14; PD - 36.3 ± 13.8; CT- 33.7 ± 14.0; TE- 19.5 ± 10.2; TE A - 34.4 ± 16.3; NK 22.2 ± 17.8; p < 0,001). There was a significant relationship between the type of renal replacement therapy and the duration of dialysis, and the concentration of TXB2, 12-HETE acid, and 15-HETE.
Conclusions: The type of renal replacement therapy significantly affects the concentration of AA derivatives. Peritoneal dialysis is the best method of dialysis, taking into account the concentration of arachidonic acid derivatives.
Keywords: 12-HETE; 15-HETE; 5-HETE; Chronic kidney disease; Kidney transplantation; Renal replacement therapy; Thromboxane B2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Szczeklik A. (red), Diseases of the kidneys of the urinary tract. Acute in the kidney and chronic kidney disease. Kraków: Interna Szczeklika, Medycyna Praktyczna; 2017. pp. 1443–1461.
-
- Dudzik M, Deeg P, Raczak G. The influence of the inflammatory process on changes in the circulatory system of patients with chronic kidney disease. Cardiol Poland. 2009;67:10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

