Amyloid-β1-43 cerebrospinal fluid levels and the interpretation of APP, PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations
- PMID: 32917274
- PMCID: PMC7488767
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-020-00676-5
Amyloid-β1-43 cerebrospinal fluid levels and the interpretation of APP, PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) mutations in amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilins (PSENs) could potentially lead to the production of longer amyloidogenic Aβ peptides. Amongst these, Aβ1-43 is more prone to aggregation and has higher toxic properties than the long-known Aβ1-42. However, a direct effect on Aβ1-43 in biomaterials of individuals carrying genetic mutations in the known AD genes is yet to be determined.
Methods: N = 1431 AD patients (n = 280 early-onset (EO) and n = 1151 late-onset (LO) AD) and 809 control individuals were genetically screened for APP and PSENs. For the first time, Aβ1-43 levels were analysed in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of 38 individuals carrying pathogenic or unclear rare mutations or the common PSEN1 p.E318G variant and compared with Aβ1-42 and Aβ1-40 CSF levels. The soluble sAPPα and sAPPβ species were also measured for the first time in mutation carriers.
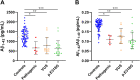
Results: A known pathogenic mutation was identified in 5.7% of EOAD patients (4.6% PSEN1, 1.07% APP) and in 0.3% of LOAD patients. Furthermore, 12 known variants with unclear pathogenicity and 11 novel were identified. Pathogenic and unclear mutation carriers showed a significant reduction in CSF Aβ1-43 levels compared to controls (p = 0.037; < 0.001). CSF Aβ1-43 levels positively correlated with CSF Aβ1-42 in both pathogenic and unclear carriers and controls (all p < 0.001). The p.E318G carriers showed reduced Aβ1-43 levels (p < 0.001), though genetic association with AD was not detected. sAPPα and sAPPβ CSF levels were significantly reduced in the group of unclear (p = 0.006; 0.005) and p.E318G carriers (p = 0.004; 0.039), suggesting their possible involvement in AD. Finally, using Aβ1-43 and Aβ1-42 levels, we could re-classify as "likely pathogenic" 3 of the unclear mutations.
Conclusion: This is the first time that Aβ1-43 levels were analysed in CSF of AD patients with genetic mutations in the AD causal genes. The observed reduction of Aβ1-43 in APP and PSENs carriers highlights the pathogenic role of longer Aβ peptides in AD pathogenesis. Alterations in Aβ1-43 could prove useful in understanding the pathogenicity of unclear APP and PSENs variants, a critical step towards a more efficient genetic counselling.
Keywords: Alzheimer mutations; Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Amyloid-β 1–43 (Aβ1–43); Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) long-read sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
MT reports personal fees (current employment) from Janssen Research & Development, a Division of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, Beerse, Belgium, and owns stock/stock options in the company.
Figures




Similar articles
-
APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations in early-onset Alzheimer disease: A genetic screening study of familial and sporadic cases.PLoS Med. 2017 Mar 28;14(3):e1002270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002270. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 28350801 Free PMC article.
-
APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 Mutations in Asian Patients with Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 25;20(19):4757. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194757. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31557888 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of γ-Secretase dysfunction as a unifying predictor of ADAD age at onset across PSEN1, PSEN2 and APP causal genes.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Apr 26;20(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00832-1. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40281586 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Genetics of Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Gene Ther. 2021;21(1):43-52. doi: 10.2174/1566523220666201123112822. Curr Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33231156 Review.
-
Pathogenic variants in the Longitudinal Early-onset Alzheimer's Disease Study cohort.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 Nov;19 Suppl 9(Suppl 9):S64-S73. doi: 10.1002/alz.13482. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 37801072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A neurodegenerative disease landscape of rare mutations in Colombia due to founder effects.Genome Med. 2022 Mar 8;14(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01035-9. Genome Med. 2022. PMID: 35260199 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease: from early pathogenesis to novel therapeutic approaches.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Aug;39(6):1231-1254. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01389-6. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39046584 Review.
-
A Possible Pathogenic PSEN2 Gly56Ser Mutation in a Korean Patient with Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 9;23(6):2967. doi: 10.3390/ijms23062967. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328387 Free PMC article.
-
The promise of gene therapy in common types of dementia.Bioimpacts. 2025 Apr 21;15:30795. doi: 10.34172/bi.30795. eCollection 2025. Bioimpacts. 2025. PMID: 40584900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics, Functions, and Clinical Impact of Presenilin-1 (PSEN1) Gene.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 19;23(18):10970. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810970. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prince PM, Wimo A, Guerchet M, Ali GM, Wu YT, Prina M. The global impact of dementia. World Alzheimer Report. 2015.
-
- Brouwers N, Sleegers K, Van Broeckhoven C. Molecular genetics of Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Ann Med. 2008;40:562–583. - PubMed
-
- Cacace R, Sleegers K, Broeckhoven C Van. Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer disease revisited. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016;12:733–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

