Early Insights from Statistical and Mathematical Modeling of Key Epidemiologic Parameters of COVID-19
- PMID: 32917290
- PMCID: PMC7588530
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2611.201074
Early Insights from Statistical and Mathematical Modeling of Key Epidemiologic Parameters of COVID-19
Abstract
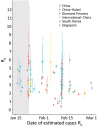
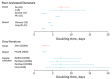
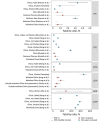
We report key epidemiologic parameter estimates for coronavirus disease identified in peer-reviewed publications, preprint articles, and online reports. Range estimates for incubation period were 1.8-6.9 days, serial interval 4.0-7.5 days, and doubling time 2.3-7.4 days. The effective reproductive number varied widely, with reductions attributable to interventions. Case burden and infection fatality ratios increased with patient age. Implementation of combined interventions could reduce cases and delay epidemic peak up to 1 month. These parameters for transmission, disease severity, and intervention effectiveness are critical for guiding policy decisions. Estimates will likely change as new information becomes available.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; World Health Organization; coronavirus; epidemiological parameters; mathematical modeling; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report 1. 2020. Jan [cited 2020 Mar 1]. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report 47. 2020. Mar [cited 2020 Mar 1]. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
-
- World Health Organization Health Emergencies Programme. Q&A on coronaviruses (COVID-19). 2020. [cited 2020 Feb 26]. https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

