Globally deimmunized lysostaphin evades human immune surveillance and enables highly efficacious repeat dosing
- PMID: 32917596
- PMCID: PMC7467700
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb9011
Globally deimmunized lysostaphin evades human immune surveillance and enables highly efficacious repeat dosing
Abstract
There is a critical need for novel therapies to treat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other drug-resistant pathogens, and lysins are among the vanguard of innovative antibiotics under development. Unfortunately, lysins' own microbial origins can elicit detrimental antidrug antibodies (ADAs) that undermine efficacy and threaten patient safety. To create an enhanced anti-MRSA lysin, a novel variant of lysostaphin was engineered by T cell epitope deletion. This "deimmunized" lysostaphin dampened human T cell activation, mitigated ADA responses in human HLA transgenic mice, and enabled safe and efficacious repeated dosing during a 6-week longitudinal infection study. Furthermore, the deimmunized lysostaphin evaded established anti-wild-type immunity, thereby providing significant anti-MRSA protection for animals that were immune experienced to the wild-type enzyme. Last, the enzyme synergized with daptomycin to clear a stringent model of MRSA endocarditis. By mitigating T cell-driven antidrug immunity, deimmunized lysostaphin may enable safe, repeated dosing to treat refractory MRSA infections.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures
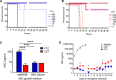
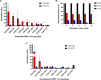
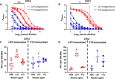


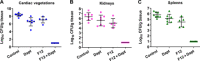
References
-
- Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 (2013); http://cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/.
-
- David M. Z., Daum R. S., Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 409, 325–383 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

