Low-cost measurement of face mask efficacy for filtering expelled droplets during speech
- PMID: 32917603
- PMCID: PMC7467698
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd3083
Low-cost measurement of face mask efficacy for filtering expelled droplets during speech
Abstract
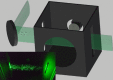
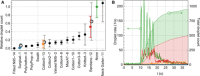
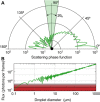
Mandates for mask use in public during the recent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, worsened by global shortage of commercial supplies, have led to widespread use of homemade masks and mask alternatives. It is assumed that wearing such masks reduces the likelihood for an infected person to spread the disease, but many of these mask designs have not been tested in practice. We have demonstrated a simple optical measurement method to evaluate the efficacy of masks to reduce the transmission of respiratory droplets during regular speech. In proof-of-principle studies, we compared a variety of commonly available mask types and observed that some mask types approach the performance of standard surgical masks, while some mask alternatives, such as neck gaiters or bandanas, offer very little protection. Our measurement setup is inexpensive and can be built and operated by nonexperts, allowing for rapid evaluation of mask performance during speech, sneezing, or coughing.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures

References
-
- Belkin N. L., The evolution of the surgical mask: Filtering efficiency versus effectiveness. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 18, 49–57 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Dharmadhikari A. S., Mphahlele M., Stoltz A., Venter K., Mathebula R., Masotla T., Lubbe W., Pagano M., First M., Jensen P. A., van der Walt M., Nardell E. A., Surgical face masks worn by patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: Impact on infectivity of air on a hospital ward. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 185, 1104–1109 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Advice on the use of masks in the context of COVID-19, WHO Reference Number: WHO/2019-nCov/IPC_Masks/2020.4 (World Health Organization, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

