Current concepts in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy
- PMID: 32918837
- PMCID: PMC8015839
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13401
Current concepts in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy
Abstract
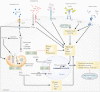
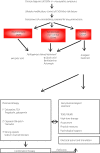
Diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy (DSPN) is encountered in approximately one-third of people with diabetes. This, in turn, might markedly impoverish their quality of life, mainly owing to neuropathic pain and foot ulcerations. Painful DSPN might be as frequent as 25% in diabetes patients. Symptoms as a result of DSPN typically comprise pain, paresthesia and numbness in the distal lower limbs. Asymptomatic DSPN might reach 50% among patients with this condition. Unfortunately, DSPN is still not adequately diagnosed and treated. Its management has three priorities: (i) lifestyle improvement, near-normoglycemia and multifactorial cardiovascular risk intervention; (ii) pathogenesis-oriented pharmacotherapy; and (iii) symptomatic alleviation of pain. Intensive diabetes therapy showed evidence for favorable effects on the incidence and deterioration of DSPN in type 1 diabetes, but not type 2 diabetes. Among pathogenesis-oriented treatments, α-lipoic acid, actovegin, benfotiamine and epalrestat are currently authorized to treat DSPN in several countries. Symptomatic therapy uses analgesics, notably antidepressants, opioids and anticonvulsants, reducing pain by ≥50% in approximately 50% of individuals, but might be limited, particularly by central nervous system-related adverse events. Local treatment with the capsaicin 8% patch might offer an alternative. In addition to pain relief, therapy should improve sleep, mobility and quality of life. In conclusion, multimodal treatment of DSPN should consider the individual risk profile, pathogenetic treatment and pain management using pharmacotherapy (combinations, if required), as well as non-pharmacological options.
Keywords: Diabetic polyneuropathy; Diagnosis; Pharmacotherapy.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dan Ziegler is a member of advisory boards of the companies Wörwag Pharma, Teva and Astellas; owns shares/equity of the companies Bayer and Pfizer; has received remunerations/fees for activities on behalf of the companies Wörwag Pharma, Meda, AstraZeneca, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Takeda, Pfizer, Lilly, Trigocare, Allergan, Novartis, Biogen, Berlin‐Chemie, Novaremed, Mundipharma and Astellas; and has received third‐party funds/project grants from Wörwag Pharma. Nikolaos Papanas has been an advisory board member of AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Takeda and TrigoCare International; has participated in sponsored studies by AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, GSK, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Novartis and Sanofi‐Aventis; has received honoraria as a speaker for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Elpen, MSD, Mylan, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sanofi‐Aventis and Vianex; and attended conferences sponsored by TrigoCare International, Eli‐Lilly, Galenica, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer and Sanofi‐Aventis. Oliver Schnell is a member of advisory boards of Wörwag Pharma. Bich Dao Thi Nguyen is a member of advisory boards of Wörwag Pharma. Khue Thy Nguyen is a member of advisory boards of the companies Wörwag Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca and Abbott; and has received remunerations/fees for activities on behalf of the companies Boehringer Ingelheim, Tosoh, MSD, Servier, Urgo and Sanofi‐Aventis. Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn is a member of advisory boards of Wörwag Pharma. Chaicharn Deerochanawong is a member of advisory boards of Wörwag Pharma.
Figures
References
-
- Consensus statement: Report and recommendations of the San Antonio conference on diabetic neuropathy. American Diabetes Association American Academy of Neurology. Diabetes Care 1988; 11: 592–597. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler D, Papanas N, Vinik AI, et al. Epidemiology of polyneuropathy in diabetes and prediabetes. Handb Clin Neurol 2014; 126: 3–22. - PubMed
-
- Nitiyanant W, Chetthakul T, Sang‐A‐kad P, et al. A survey study on diabetes management and complication status in primary care setting in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai 2007; 90: 65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

