Environmental and Intestinal Phylum Firmicutes Bacteria Metabolize the Plant Sugar Sulfoquinovose via a 6-Deoxy-6-sulfofructose Transaldolase Pathway
- PMID: 32919372
- PMCID: PMC7491151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101510
Environmental and Intestinal Phylum Firmicutes Bacteria Metabolize the Plant Sugar Sulfoquinovose via a 6-Deoxy-6-sulfofructose Transaldolase Pathway
Abstract
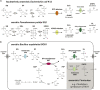
Bacterial degradation of the sugar sulfoquinovose (SQ, 6-deoxy-6-sulfoglucose) produced by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is an important component of the biogeochemical carbon and sulfur cycles. Here, we reveal a third biochemical pathway for primary SQ degradation in an aerobic Bacillus aryabhattai strain. An isomerase converts SQ to 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose (SF). A novel transaldolase enzyme cleaves the SF to 3-sulfolactaldehyde (SLA), while the non-sulfonated C3-(glycerone)-moiety is transferred to an acceptor molecule, glyceraldehyde phosphate (GAP), yielding fructose-6-phosphate (F6P). Intestinal anaerobic bacteria such as Enterococcus gilvus, Clostridium symbiosum, and Eubacterium rectale strains also express transaldolase pathway gene clusters during fermentative growth with SQ. The now three known biochemical strategies for SQ catabolism reflect adaptations to the aerobic or anaerobic lifestyle of the different bacteria. The occurrence of these pathways in intestinal (family) Enterobacteriaceae and (phylum) Firmicutes strains further highlights a potential importance of metabolism of green-diet SQ by gut microbial communities to, ultimately, hydrogen sulfide.
Keywords: Microbial Metabolism; Microbiology.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anaerobic Faecalicatena spp. degrade sulfoquinovose via a bifurcated 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose transketolase/transaldolase pathway to both C2- and C3-sulfonate intermediates.Front Microbiol. 2024 Dec 5;15:1491101. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1491101. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39712897 Free PMC article.
-
A transaldolase-dependent sulfoglycolysis pathway in Bacillus megaterium DSM 1804.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 17;533(4):1109-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.124. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 33036753
-
Structure and mechanism of sulfofructose transaldolase, a key enzyme in sulfoquinovose metabolism.Structure. 2023 Mar 2;31(3):244-252.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2023.01.010. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Structure. 2023. PMID: 36805128
-
New mechanisms for bacterial degradation of sulfoquinovose.Biosci Rep. 2022 Oct 28;42(10):BSR20220314. doi: 10.1042/BSR20220314. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36196895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfoglycolysis: catabolic pathways for metabolism of sulfoquinovose.Chem Soc Rev. 2021 Dec 13;50(24):13628-13645. doi: 10.1039/d1cs00846c. Chem Soc Rev. 2021. PMID: 34816844 Review.
Cited by
-
Anaerobic Faecalicatena spp. degrade sulfoquinovose via a bifurcated 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose transketolase/transaldolase pathway to both C2- and C3-sulfonate intermediates.Front Microbiol. 2024 Dec 5;15:1491101. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1491101. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39712897 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, kinetics, and mechanism of Pseudomonas putida sulfoquinovose dehydrogenase, the first enzyme in the sulfoglycolytic Entner-Doudoroff pathway.Biochem J. 2025 Jan 22;482(2):57-72. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240605. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 39840830 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide on the Microbiome: From Toxicity to Therapy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Feb;36(4-6):211-219. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0004. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 33691464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Variant of the Sulfoglycolytic Transketolase Pathway for the Degradation of Sulfoquinovose into Sulfoacetate.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul 26;89(7):e0061723. doi: 10.1128/aem.00617-23. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37404184 Free PMC article.
-
The sulfoquinovosyl glycerol binding protein SmoF binds and accommodates plant sulfolipids.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2022 Mar 7;4:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2022.03.001. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35341160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attene-Ramos M.S., Nava G.M., Muellner M.G., Wagner E.D., Plewa M.J., Gaskins H.R. DNA damage and toxicogenomic analyses of hydrogen sulfide in human intestinal epithelial FHs 74 Int cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2010;51:304–314. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Even A., Flamholz A., Noor E., Milo R. Rethinking glycolysis: on the biochemical logic of metabolic pathways. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012;17:509–517. - PubMed
-
- Barańskaa J., Dzugajb A., Kwiatkowska-Korczakc J. Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas, the first metabolic pathway: the fate of prominent polish biochemist Jakub Karol Parnas. Compr. Biochem. 2007;45:157–207.
-
- Benning C. Biosynthesis and function of the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1998;49:53–75. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

