Differential and unique patterns of synaptic miRNA expression in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of depressed subjects
- PMID: 32919404
- PMCID: PMC8115313
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-020-00861-y
Differential and unique patterns of synaptic miRNA expression in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of depressed subjects
Abstract
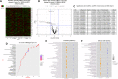
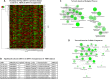
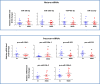
Altered synaptic plasticity is often associated with major depressive disorder (MDD). Disease-associated changes in synaptic functions are tightly correlated with altered microRNA (miRNA) expression. Here, we examined the role of miRNAs and their functioning at the synapse in MDD by examining miRNA processing machinery at synapse and sequencing miRNAs and analyzing their functions in synaptic and total tissue fractions obtained from dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) of 15 MDD and 15 matched non-psychiatric control subjects. A total of 333 miRNAs were reliably detected in the total tissue fraction. Multiple testing following the Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate [FDR] showed that 18 miRNAs were significantly altered (1 downregulated 4 up and 13 downregulated; p < 0.05) in MDD subjects. Out of 351 miRNAs reliably expressed in the synaptic fraction, 24 were uniquely expressed at synapse. In addition, 8 miRNAs (miR-215-5p, miR-192-5p, miR-202-5p, miR-19b-3p, miR-423-5p, miR-219a-2-3p; miR-511-5p, miR-483-5p showed significant (FDR corrected; p < 0.05) differential regulation in the synaptic fraction from dlPFC of MDD subjects. In vitro transfection studies and gene ontology revealed involvement of these altered miRNAs in synaptic plasticity, nervous system development, and neurogenesis. A shift in expression ratios (synaptic vs. total fraction) of miR-19b-3p, miR-376c-3p, miR-455-3p, and miR-337-3p were also noted in the MDD group. Moreover, an inverse relationship between the expression of precursor (pre-miR-19b-1, pre-miR-199a-1 and pre-miR-199a-2) and mature (miR-19b-3p, miR-199a-3p) miRNAs was found. Although not significantly, several miRNA processing enzymes (DROSHA [95%], DICER [17%], TARBP2 [38%]) showed increased expression patterns in MDD subjects. Our findings provide new insights into the understanding of the regulation of miRNAs at the synapse and their possible roles in MDD pathogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular pathology associated with altered synaptic transcriptome in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of depressed subjects.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Jan 22;11(1):73. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-01159-9. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33483466 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic plasticity and depression: the role of miRNAs dysregulation.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Oct;49(10):9759-9765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07461-7. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35441941 Review.
-
Identification of differential microRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with major depressive disorder.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 12;10(3):e0121975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121975. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25763923 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of differential expression profile of miRNA in peripheral blood of patients with lung cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Nov;33(9):e23003. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23003. Epub 2019 Sep 20. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 31541491 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the differentially expressed peripheral blood microRNAs in psychiatric disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 May 17;15:1390366. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1390366. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38827444 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of miR-592-3p and Its Target Gene, TMEFF1, in the Nucleus Accumbens During Incubation of Morphine Craving.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022 May 27;25(5):412-424. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyac004. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35020881 Free PMC article.
-
Genes associated with cellular senescence as diagnostic markers of major depressive disorder and their correlations with immune infiltration.Front Psychiatry. 2024 May 31;15:1372386. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1372386. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38881549 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Circulating miRNAs as Molecular Markers in Mood Disorders and Associated Suicidal Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 28;24(5):4664. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054664. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals That Act on Synaptic Plasticity as Potential Prophylaxis against Stress-Induced Depressive Disorder.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023 Mar 1;31(2):148-160. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.116. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 36694423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Pre-Treatment miRNAs Levels in Untreated Major Depressive Disorder Patients Predict Early Response to Antidepressants and Interact with Key Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3873. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073873. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409234 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Park CS, Gong R, Stuart J, Tang SJ. Molecular network and chromosomal clustering of genes involved in synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:30195–211. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Rana TM. Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs: current status and future challenges. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2014;13:622–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

