Antibody-dependent enhancement of coronavirus
- PMID: 32920233
- PMCID: PMC7483033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.015
Antibody-dependent enhancement of coronavirus
Abstract
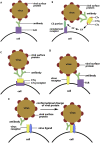
Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) exists in several kinds of virus. It has a negative influence on antibody therapy for viral infection. This effect was first identified in dengue virus and has since also been described for coronavirus. To date, the rapid spread of the newly emerged coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), causing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has affected over 3.8 million people across the globe. The novel coronavirus poses a great challenge and has caused a wave of panic. In this review, antibody-dependent enhancements in dengue virus and two kinds of coronavirus are summarized. Possible solutions for the effects are reported. We also speculate that ADE may exist in SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE); Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV); Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV); Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Chan J.F.-W., Zhang A.J., Yuan S., Poon V.K.-M., Chan C.C.-S., Lee A.C.-Y., et al. Simulation of the clinical and pathological manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in golden Syrian hamster model: implications for disease pathogenesis and transmissibility. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa325. pii: ciaa325. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous