Photoreactivity of Bis-retinoid A2E Complexed with a Model Protein in Selected Model Systems
- PMID: 32920760
- PMCID: PMC7567710
- DOI: 10.1007/s12013-020-00942-1
Photoreactivity of Bis-retinoid A2E Complexed with a Model Protein in Selected Model Systems
Abstract
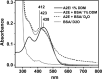
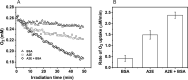
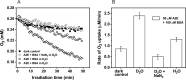
The bis-retinoid N-retinyl-N-retinylidene ethanolamine (A2E) is formed as a byproduct of visual cycle in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). It contributes to golden-yellow fluorescence of the age pigment lipofuscin, which accumulates in RPE. Lipofuscin can generate a variety of reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon blue-light excitation. Although in model systems photoreactivity of A2E has been determined to be low, this bis-retinoid exhibited significant phototoxicity in RPE cells in vitro. Although the mechanism of A2E-mediated phototoxicity remains mostly unknown, we hypothesize that formation of A2E-adducts with different biomolecules may play an important role. In this study, we investigated the photochemical reactivity of A2E and its complex with bovine serum albumin (BSA) using UV-Vis absorption and emission spectroscopy, EPR-spin trapping, EPR-oximetry, time-resolved singlet oxygen phosphorescence, and the fluorogenic CBA probe. Our data show that A2E after complexation with this model protein photogenerated an increased level of ROS, particularly singlet oxygen. We also demonstrated the ability of A2E to oxidize BSA upon excitation with blue light in aqueous model systems. The data suggest that pyridinium bis-retinoid could oxidatively modify cellular proteins under physiological conditions.
Keywords: A2E; EPR-Spin trapping; Photochemical reactivity; Protein oxidation; Reactive oxygen species; Singlet oxygen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of the aerobic photoreactivity of A2E with its precursor retinal.Photochem Photobiol. 2003 Mar;77(3):253-8. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2003)077<0253:cotapo>2.0.co;2. Photochem Photobiol. 2003. PMID: 12685651
-
A2E and Lipofuscin.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;134:449-63. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26310170 Review.
-
Immunochemical recognition of A2E, a pigment in the lipofuscin of retinal pigment epithelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 11;104(37):14610-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706806104. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17804788 Free PMC article.
-
Lipofuscin and N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E) accumulate in retinal pigment epithelium in absence of light exposure: their origin is 11-cis-retinal.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 22;287(26):22276-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.329235. Epub 2012 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22570475 Free PMC article.
-
A2E: a component of ocular lipofuscin.Photochem Photobiol. 2004 Feb;79(2):127-36. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2004)079<0127:aacool>2.0.co;2. Photochem Photobiol. 2004. PMID: 15068025 Review.
Cited by
-
Water-Soluble Products of Photooxidative Destruction of the Bisretinoid A2E Cause Proteins Modification in the Dark.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1534. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031534. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163454 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Purple Corn (Zea mays L.) Byproduct Extract on Blue Light-Induced Retinal Damage in A2E-Accumulated ARPE-19 Cells.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024 Sep 30;29(3):376-383. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2024.29.3.376. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39371508 Free PMC article.
-
Bisretinoids of the Retina: Photo-Oxidation, Iron-Catalyzed Oxidation, and Disease Consequences.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 29;10(9):1382. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091382. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Oxidative Stress Mediated by UVA-Visible Light Leads to Keratinocyte Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10645. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910645. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638985 Free PMC article.
-
The Supportive Role of Plant-Based Substances in AMD Treatment and Their Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 16;26(16):7906. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167906. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boulton M, Dontsov A, Jarvis-Evans J, Ostrovsky M, Svistunenko D. Lipofuscin is a photoinducible free radical generator. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1993;19:201–204. - PubMed
-
- Rozanowska M, Jarvis-Evans J, Korytowski W, Boulton M, Burke J, Sarna T. Blue light-induced reactivity of retinal age pigment. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:18825–18830. - PubMed
-
- Wassell J, Davies S, Bardsley W, Boulton M. Photoreactivity of the retinal age pigment lipofuscin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:23828–23832. - PubMed
-
- Dontsov A, Glickman R, Ostrovsky M. Retinal pigment epithelium pigment granules stimulate the photo-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1999;26:1436–1446. - PubMed
-
- Eldered G. Lipofuscin fluorophore inhibits lysosomal protein degradation and may cause early stages of macular degeneration. Gerontology. 1995;41:15–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

