Downregulation of miR-326 and its host gene β-arrestin1 induces pro-survival activity of E2F1 and promotes medulloblastoma growth
- PMID: 32920979
- PMCID: PMC7858128
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12800
Downregulation of miR-326 and its host gene β-arrestin1 induces pro-survival activity of E2F1 and promotes medulloblastoma growth
Abstract
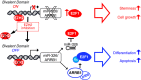
Persistent mortality rates of medulloblastoma (MB) and severe side effects of the current therapies require the definition of the molecular mechanisms that contribute to tumor progression. Using cultured MB cancer stem cells and xenograft tumors generated in mice, we show that low expression of miR-326 and its host gene β-arrestin1 (ARRB1) promotes tumor growth enhancing the E2F1 pro-survival function. Our models revealed that miR-326 and ARRB1 are controlled by a bivalent domain, since the H3K27me3 repressive mark is found at their regulatory region together with the activation-associated H3K4me3 mark. High levels of EZH2, a feature of MB, are responsible for the presence of H3K27me3. Ectopic expression of miR-326 and ARRB1 provides hints into how their low levels regulate E2F1 activity. MiR-326 targets E2F1 mRNA, thereby reducing its protein levels; ARRB1, triggering E2F1 acetylation, reverses its function into pro-apoptotic activity. Similar to miR-326 and ARRB1 overexpression, we also show that EZH2 inhibition restores miR-326/ARRB1 expression, limiting E2F1 pro-proliferative activity. Our results reveal a new regulatory molecular axis critical for MB progression.
Keywords: ARRB1; E2F1; EZH2; medulloblastoma; miR-326.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β-arrestin1-mediated acetylation of Gli1 regulates Hedgehog/Gli signaling and modulates self-renewal of SHH medulloblastoma cancer stem cells.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jul 17;17(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3477-0. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28716052 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of miR-204 expression defines a highly aggressive subset of Group 3/Group 4 medulloblastomas.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Apr 3;7(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0697-3. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 30944042 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits proliferation and migration of medulloblastoma Daoy by down-regulation of microRNA-31.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Aug;119(8):6527-6534. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26716. Epub 2018 Apr 19. J Cell Biochem. 2018. Retraction in: J Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;122 Suppl 1:S18. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29977. PMID: 29377269 Retracted.
-
Transcriptional repressor REST drives lineage stage-specific chromatin compaction at Ptch1 and increases AKT activation in a mouse model of medulloblastoma.Sci Signal. 2019 Jan 22;12(565):eaan8680. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aan8680. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 30670636 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 accelerates the glioma carcinogenesis by competing endogenous sponging miR-197-5p to relieve E2F1.Gene. 2019 Feb 20;686:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.065. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30366080
Cited by
-
β-arrestin1-E2F1-ac axis regulates physiological apoptosis and cell cycle exit in cellular models of early postnatal cerebellum.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 27;11:990711. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.990711. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36923256 Free PMC article.
-
Splice and Dice: Intronic microRNAs, Splicing and Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 19;9(9):1268. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091268. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAFG-DT promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 13;14:1461546. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1461546. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39735608 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-326: Role and significance in brain cancers.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 Feb 25;12:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.02.006. eCollection 2025 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40115178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles for Drug and Gene Delivery in Pediatric Brain Tumors' Cancer Stem Cells: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 2;15(2):505. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020505. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones D, Schlanstein M, Northcott P, Cho Y‐J, Koster J, Schouten‐van Meeteren A, van Vuurden D et al (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta‐analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol 123, 473–484. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hovestadt V, Remke M, Kool M, Pietsch T, Northcott PA, Fischer R, Cavalli FMG, Ramaswamy V, Zapatka M, Reifenberger G et al (2013) Robust molecular subgrouping and copy‐number profiling of medulloblastoma from small amounts of archival tumour material using high‐density DNA methylation arrays. Acta Neuropathol 125, 913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Northcott PA, Robinson GW, Kratz CP, Mabbott DJ, Pomeroy SL, Clifford SC, Rutkowski S, Ellison DW, Malkin D, Taylor MD et al (2019) Medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5, 1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

