Aliskiren, tadalafil, and cinnamaldehyde alleviate joint destruction biomarkers; MMP-3 and RANKL; in complete Freund's adjuvant arthritis model: Downregulation of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 32922141
- PMCID: PMC7474170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.07.011
Aliskiren, tadalafil, and cinnamaldehyde alleviate joint destruction biomarkers; MMP-3 and RANKL; in complete Freund's adjuvant arthritis model: Downregulation of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
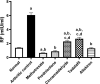
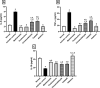
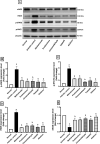
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease, which is accompanied by progressive joint damage and disability. The intolerability of conventional antirheumatic drugs by some patients necessitates the search for effective antirheumatic agents having better tolerability. In the current work, we aimed to investigate the efficacy of cinnamaldehyde, tadalafil, and aliskiren as potential antirheumatic candidates and to explore their modulatory effects on joint destruction, inflammatory response, and intracellular signaling. Arthritis was induced in female Wistar rats by complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) 0.4 ml s.c. on days 1, 4, and 7. Treated groups received their respective drugs, starting from day 13, daily for 3 weeks. Methotrexate and prednisolone were the standard antirheumatic drugs, while cinnamaldehyde, tadalafil, and aliskiren were the test agents. Treatment with cinnamaldehyde, tadalafil, or aliskiren reduced serum levels of rheumatoid factor, and pro-inflammatory cytokines; tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 (IL-6), along with elevated level of IL-10 which is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. Besides, cartilage and bone destruction biomarkers; matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL); were significantly reduced after treatment with the test agents, which was further confirmed by histopathological investigation. The elevated protein expressions of phosphorylated-Janus kinase 2 (p-JAK2), phosphorylated-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in articular tissue were markedly attenuated after treatment with cinnamaldehyde, tadalafil, or aliskiren, while that of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) was greatly enhanced. In addition, oxidative stress and inflammatory markers such as malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, and myeloperoxidase were reduced in joint tissue after treatment with the test agents, while glutathione content was elevated. Furthermore, the renin inhibitor aliskiren produced effects close to those of the normal and methotrexate, the gold standard antirheumatic drug, in most of the measured parameters. Collectively, these findings led to the assumption that the downregulation of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling by cinnamaldehyde, tadalafil, and aliskiren could alleviate joint destruction by MMP-3 and RANKL, reduce iNOS, and enhance eNOS expressions. Moreover, aliskiren could be a promising therapeutic agent for RA, because of its ability to normalize most of the measured parameters after CFA-induced arthritis.
Keywords: Aliskiren; CFA, complete Freund's adjuvant; CFA-induced arthritis; DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; GSH, reduced glutathione; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; IL-10, interleukin-10; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; MDA, malondialdehyde; MMP-3; MMP-3, matrix metalloproteinase-3; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NO, nitric oxide; PDE, phosphodiesterase; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RANKL; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand; RAS, renin angiotensin system; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nicorandil and theophylline can protect experimental rats against complete Freund's adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis through modulation of JAK/STAT/RANKL signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 5;822:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29337196
-
Novel Anti-arthritic Mechanisms of Polydatin in Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats: Involvement of IL-6, STAT-3, IL-17, and NF-кB.Inflammation. 2018 Oct;41(5):1974-1986. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0841-4. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29982962
-
Venlafaxine alleviates complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: Modulation of STAT-3/IL-17/RANKL axis.Life Sci. 2019 Jun 1;226:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.063. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30928406
-
Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Feb 21;14:100223. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100223. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35243298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects of moxibustion on serum cytokines in experimental animals with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020 Sep 25;45(9):751-61. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190780. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32959560 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Integrated Experimental Approach, Phytochemistry, and Network Pharmacology to Explore the Potential Mechanisms of Cinnamomi Ramulus for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 15;2022:6060677. doi: 10.1155/2022/6060677. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36160710 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of renal nitric oxide and eNOS/iNOS expression by tadalafil participates in the mitigation of amphotericin B-induced renal injury: Down-regulation of NF-κB/iNOS/caspase-3 signaling.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 May;397(5):3141-3153. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02787-w. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37891258 Free PMC article.
-
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and arthritic diseases: therapeutic potential for RAS inhibitors.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01890-z. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40796991 Review.
-
Network pharmacology-based analysis of the mechanism of Saposhnikovia divaricata for the treatment of type I allergy.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1224-1236. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2086583. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35760567 Free PMC article.
-
Fascin1 mediated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and invasion/migration in rheumatoid arthritis via the STAT3 pathway.Cell Cycle. 2021 Nov;20(21):2210-2220. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1974790. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Cell Cycle. 2021. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2024 Sep-Oct;23(17-20):ii. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2025.2460937. PMID: 34499588 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Abd El-Raouf O.M., El-Sayed E.S.M., Manie M.F. Cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde ameliorate cisplatin-induced splenotoxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015;29:426–431. - PubMed
-
- Afify H., Abo-Youssef A.M., Abdel-Rahman H.M., Allam S., Azouz A.A. The modulatory effects of cinnamaldehyde on uric acid level and IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signaling as a promising therapeutic strategy against benign prostatic hyperplasia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020;402 - PubMed
-
- Aguirre J., Buttery L., O’Shaughnessy M., Afzal F., de Marticorena I.F., Hukkanen M., Huang P., MacIntyre I., Polak J. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene-deficient mice demonstrate marked retardation in postnatal bone formation, reduced bone volume, and defects in osteoblast maturation and activity. Am. J. Pathol. 2001;158:247–257. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akpinar E., Halici Z., Cadirci E., Bayir Y., Karakus E., Calik M., Topcu A., Polat B. What is the role of renin inhibition during rat septic conditions: preventive effect of aliskiren on sepsis-induced lung injury. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2014;387:969–978. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

