Exploring the Role of Chemokine Receptor 6 (Ccr6) in the BXD Mouse Model of Gulf War Illness
- PMID: 32922257
- PMCID: PMC7456958
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00818
Exploring the Role of Chemokine Receptor 6 (Ccr6) in the BXD Mouse Model of Gulf War Illness
Abstract
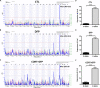
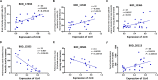
Gulf War illness (GWI) is a chronic and multi-symptomatic disorder with persistent neuroimmune symptomatology. Chemokine receptor 6 (CCR6) has been shown to be involved in several inflammation disorders in humans. However, the causative relationship between CCR6 and neuroinflammation in GWI has not yet been investigated. By using RNA-seq data of prefrontal cortex (PFC) from 31 C57BL/6J X DBA/2J (BXD) recombinant inbred (RI) mouse strains and their parental strains under three chemical treatment groups - saline control (CTL), diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP), and corticosterone combined with diisopropylfluorophosphate (CORT+DFP), we identified Ccr6 as a candidate gene underlying individual differences in susceptibility to GWI. The Ccr6 gene is cis-regulated and its expression is significantly correlated with CORT+DFP treatment. Its mean transcript abundance in PFC of BXD mice decreased 1.6-fold (p < 0.0001) in the CORT+DFP group. The response of Ccr6 to CORT+DFP is also significantly different (p < 0.0001) between the parental strains, suggesting Ccr6 is affected by both host genetic background and chemical treatments. Pearson product-moment correlation analysis revealed 1473 Ccr6-correlated genes (p < 0.05). Enrichment of these genes was seen in the immune, inflammation, cytokine, and neurological related categories. In addition, we also found five central nervous system-related phenotypes and fecal corticosterone concentration have significant correlation (p < 0.05) with expression of Ccr6 in the PFC. We further established a protein-protein interaction subnetwork for the Ccr6-correlated genes, which provides an insight on the interaction of G protein-coupled receptors, kallikrein-kinin system and neuroactive ligand-receptors. This analysis likely defines the heterogeneity and complexity of GWI. Therefore, our results suggest that Ccr6 is one of promising GWI biomarkers.
Keywords: BXD strain; CORT; Ccr6; DFP; GWI; RNA-seq; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Gao, Xu, Starlard-Davenport, Miller, O’Callaghan, Jones and Lu.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide transcriptome architecture in a mouse model of Gulf War Illness.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Oct;89:209-223. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.06.018. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 32574576 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosterone primes the neuroinflammatory response to DFP in mice: potential animal model of Gulf War Illness.J Neurochem. 2015 Jun;133(5):708-21. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13088. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25753028 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosterone primes the neuroinflammatory response to Gulf War Illness-relevant organophosphates independently of acetylcholinesterase inhibition.J Neurochem. 2017 Aug;142(3):444-455. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14071. Epub 2017 Jun 14. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28500787 Free PMC article.
-
Oligodendrocyte involvement in Gulf War Illness.Glia. 2019 Nov;67(11):2107-2124. doi: 10.1002/glia.23668. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Glia. 2019. PMID: 31339622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of cellular energetics in Gulf War Illness.Toxicology. 2021 Sep;461:152894. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152894. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 34389359 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of distinct neuroinflammatory markers and gut dysbiosis by differential pyridostigmine bromide dosing in a chronic mouse model of GWI showing persistent exercise fatigue and cognitive impairment.Life Sci. 2022 Jan 1;288:120153. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120153. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 34801513 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Neuroimmune Interactions in Human Subjects and Animal Models to Predict Subtype-Specific Multidrug Treatments for Gulf War Illness.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 9;22(16):8546. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168546. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445252 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic study of the long-term effects of gulf War illness.Front Genet. 2025 Jun 18;16:1553410. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1553410. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40606660 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic analysis in a murine genetic model of Gulf War illness.Front Toxicol. 2023 Jun 14;5:1162749. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2023.1162749. eCollection 2023. Front Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37389175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apkarian A. V., Bushnell M. C., Treede R.-D., Zubieta J.-K. (2005). Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur. J. Pain 9 463–484. - PubMed
-
- Ashbrook D. G., Arends D., Prins P., Mulligan M. K., Roy S., Williams E. G., et al. (2019). The expanded BXD family of mice: a cohort for experimental systems genetics and precision medicine. BioRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/672097 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

