Targeting Cytokine Release Through the Differential Modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways by Electrophilic/Non-Electrophilic Compounds
- PMID: 32922294
- PMCID: PMC7456937
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01256
Targeting Cytokine Release Through the Differential Modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways by Electrophilic/Non-Electrophilic Compounds
Abstract
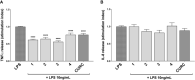
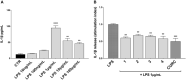
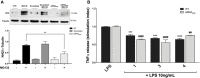
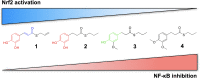
The transcription factor Nrf2 coordinates a multifaceted response to various forms of stress and to inflammatory processes, maintaining a homeostatic intracellular environment. Nrf2 anti-inflammatory activity has been related to the crosstalk with the transcription factor NF-κB, a pivotal mediator of inflammatory responses and of multiple aspects of innate and adaptative immune functions. However, the underlying molecular basis has not been completely clarified. By combining into new chemical entities, the hydroxycinnamoyl motif from curcumin and the allyl mercaptan moiety of garlic organosulfur compounds, we tested a set of molecules, carrying (pro)electrophilic features responsible for the activation of the Nrf2 pathway, as valuable pharmacologic tools to dissect the mechanistic connection between Nrf2 and NF-κB. We investigated whether the activation of the Nrf2 pathway by (pro)electrophilic compounds may interfere with the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, during immune stimulation, in a human immortalized monocyte-like cell line (THP-1). The capability of compounds to affect the NF-κB pathway was also evaluated. We assessed the compounds-mediated regulation of cytokine and chemokine release by using Luminex X-MAP® technology in human primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) upon LPS stimulation. We found that all compounds, also in the absence of electrophilic moieties, significantly suppressed the LPS-evoked secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and IL-1β, but not of IL-8, in THP-1 cells. A reduction in the release of pro-inflammatory mediators similar to that induced by the compounds was also observed after siRNA mediated-Nrf2 knockdown, thus indicating that the attenuation of cytokine secretion cannot be directly ascribed to the activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Moreover, all compounds, with the exception of compound 1, attenuated the LPS-induced activation of the NF-κB pathway, by reducing the upstream phosphorylation of IκB, the NF-κB nuclear translocation, as well as the activation of NF-κB promoter. In human PBMCs, compound 4 and CURC attenuated TNFα release as observed in THP-1 cells, and all compounds acting as Nrf2 inducers significantly decreased the levels of MCP-1/CCL2, as well as the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-12. Altogether, the compounds induced a differential modulation of innate immune cytokine release, by differently regulating Nrf2 and NF-κB intracellular signaling pathways.
Keywords: MCP-1; NF-κB; Nrf2; TNFα; antioxidant; curcumin; cytokine release; inflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Fagiani, Catanzaro, Buoso, Basagni, Di Marino, Raniolo, Amadio, Frost, Corsini, Racchi, Fulop, Govoni, Rosini and Lanni.
Figures



Similar articles
-
4-Octyl Itaconate Activates Nrf2 Signaling to Inhibit Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(2):979-990. doi: 10.1159/000495400. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30466076
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of Khayandirobilide A from Khaya senegalensis via NF-κB, AP-1 and p38 MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 and BV-2 cells.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;42:152-163. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29655681
-
Activation of the Nrf2 response by intrinsic hepatotoxic drugs correlates with suppression of NF-κB activation and sensitizes toward TNFα-induced cytotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2016 May;90(5):1163-79. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1536-3. Epub 2015 May 31. Arch Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26026609 Free PMC article.
-
Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jul 18;16(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1538-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31319868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammation effects of dietary phytochemicals: The Nrf2/NF-κB signalling pathway and upstream factors of Nrf2.Phytochemistry. 2022 Dec;204:113429. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113429. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Phytochemistry. 2022. PMID: 36096269 Review.
Cited by
-
Nature-Inspired Hybrids (NIH) Improve Proteostasis by Activating Nrf2-Mediated Protective Pathways in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;11(7):1385. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071385. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883876 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Bisphenols on RACK1 Expression and Their Immunological Implications in THP-1 Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 21;12:743991. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.743991. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34621174 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin attenuated ischemic stroke induced neurodegeneration by modulating glutamatergic and synaptic signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 20;10(7):e28016. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28016. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. Retraction in: Heliyon. 2025 Mar 25;11(9):e43266. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e43266. PMID: 38571617 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A Nature-Inspired Nrf2 Activator Protects Retinal Explants from Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 16;10(8):1296. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081296. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439544 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Epithelial Barrier Integrity via Altered GILZ/c-Rel/RACK1 Signaling in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Crohns Colitis. 2025 Jan 11;19(1):jjae191. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae191. J Crohns Colitis. 2025. PMID: 39693354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binkley J. S., Pople J. A., Hehre W. J. (1980). Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. 21. Small split-valence basis sets for first-row elements. J. Am. Chem. Soc 102, 939–947. 10.1021/ja00523a008 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

