Alleviation of Depression by Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Through the Regulation of Neuroinflammation, Neurotransmitters, Neurogenesis, and Synaptic Function
- PMID: 32922295
- PMCID: PMC7456867
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01270
Alleviation of Depression by Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Through the Regulation of Neuroinflammation, Neurotransmitters, Neurogenesis, and Synaptic Function
Abstract
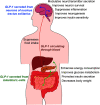
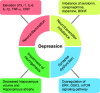
Depression has emerged as a major cause of mortality globally. Many studies have reported risk factors and mechanisms associated with depression, but it is as yet unclear how these findings can be applied to the treatment and prevention of this disorder. The onset and recurrence of depression have been linked to diverse metabolic factors, including hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance. Recent studies have suggested that depression is accompanied by memory loss as well as depressive mood. Thus, many researchers have highlighted the relationship between depressive behavior and metabolic alterations from various perspectives. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is secreted from gut cells and hindbrain areas, has been studied in metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes, and was shown to control glucose metabolism and insulin resistance. Recently, GLP-1 was highlighted as a regulator of diverse pathways, but its potential as the therapeutic target of depressive disorder was not described comprehensively. Therefore, in this review, we focused on the potential of GLP-1 modulation in depression.
Keywords: depression; glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1); neurogenesis; neuroinflammation; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2020 Kim, Kim and Song.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP1) in Type 3 Diabetes: GLP-1 Controls Insulin Resistance, Neuroinflammation and Neurogenesis in the Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 22;18(11):2493. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112493. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29165354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive dysfunction and metabolic comorbidities in mood disorders: A repurposing opportunity for glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists?Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jul 1;136(Pt B):335-342. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.01.048. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29481915 Review.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Neurosci. 2019 Oct 18;13:1112. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01112. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31680842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in an animal model of depression and their effect on corticotropin-releasing hormone promoter gene activity in a hypothalamic cell line.Pharmacol Rep. 2019 Apr;71(2):338-346. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Pharmacol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30831439
-
Engineered beta-cells secreting dipeptidyl peptidase IV-resistant glucagon-like peptide-1 show enhanced glucose-responsiveness.Life Sci. 2005 Jan 28;76(11):1239-48. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.08.021. Epub 2004 Dec 8. Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15642594
Cited by
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and their cardiovascular benefits-The role of the GLP-1 receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):659-676. doi: 10.1111/bph.15462. Epub 2021 May 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33764504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut-Brain Interactions and Their Impact on Astrocytes in the Context of Multiple Sclerosis and Beyond.Cells. 2024 Mar 13;13(6):497. doi: 10.3390/cells13060497. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depression-associated gut microbes, metabolites and clinical trials.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 31;15:1292004. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1292004. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38357350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormonal Regulation of Oxidative Phosphorylation in the Brain in Health and Disease.Cells. 2021 Oct 28;10(11):2937. doi: 10.3390/cells10112937. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of Shengmai San and Radix puerariae ameliorates depression-like symptoms in diabetic rats at the nexus of PI3K/BDNF/SYN protein expression.Animal Model Exp Med. 2023 Jun;6(3):211-220. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12333. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Animal Model Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37317044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akarte A. S., Srinivasan B. P., Gandhi S., Sole S. (2012). Chronic DPP-IV inhibition with PKF-275-055 attenuates inflammation and improves gene expressions responsible for insulin secretion in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 47, 456–463. 10.1016/j.ejps.2012.07.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akimoto H., Tezuka K., Nishida Y., Nakayama T., Takahashi Y., Asai S. (2019). Association between use of oral hypoglycemic agents in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of depression: A retrospective cohort study. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 7, e00536. 10.1002/prp2.536 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

